"VSports最新版本" Downregulation of miR-194-5p induces paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells by altering MDM2 expression
- PMID: 30774764
- PMCID: "VSports" PMC6363016
- DOI: V体育ios版 - 10.18632/oncotarget.26586
Downregulation of miR-194-5p induces paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells by altering MDM2 expression
VSports - Abstract
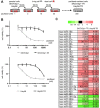
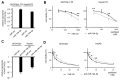
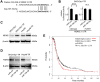
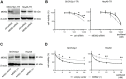
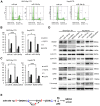
Paclitaxel is a first-line drug for treating epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). However, prognosis for patients with advanced stage cancer remains poor due to primary or acquired drug resistance. Therefore, overcoming chemoresistance is one of the greatest challenges in treating EOC. In this study, we identified microRNAs (miRNA) that regulate paclitaxel resistance and tested their potential utility as therapeutic targets. Paclitaxel-resistant cell lines were established using two EOC cell lines: SKVO3ip1 and HeyA8. miRNA PCR arrays showed that miR-194-5p was downregulated in paclitaxel-resistant cells. Forced expression of miR-194-5p resensitized resistant cells to paclitaxel. Conversely, miR-194-5p inhibition induced paclitaxel resistance in parental cells. In silico analysis and luciferase reporter assay revealed that MDM2 is a direct target of miR-194-5p. MDM2 was upregulated in paclitaxel resistant cells compared with parental cells. MDM2 inhibition also resensitized resistant cells to paclitaxel and forced MDM2 induced paclitaxel resistance in parental cells. miR-194-5p induced p21 upregulation and G1 phase arrest in resistant cells by downregulating MDM2 VSports手机版. Furthermore, a public database showed that high MDM2 expression was associated with a shorter progression-free survival in EOC patients treated with paclitaxel. Collectively, our results show that restoring miR-194-5p expression resensitizes EOCs to paclitaxel, and this may be exploited as a therapeutic option. .
Keywords: MDM2; miR-194-5p; microRNA; ovarian cancer; paclitaxel resistance V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Bookman MA. Optimal primary therapy of ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:i158–i162. - PubMed
-
- Cannistra SA. Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2519–2529. - PubMed
-
- Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:287–314. - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magee P, Shi L, Garofalo M. Role of microRNAs in chemoresistance. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3:332. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

