"VSports app下载" Ikaros family zinc finger 1 regulates dendritic cell development and function in humans
- PMID: 29588478
- PMCID: "V体育ios版" PMC5869589
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-02977-8
Ikaros family zinc finger 1 regulates dendritic cell development and function in humans (V体育ios版)
"VSports手机版" Abstract
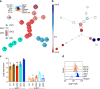
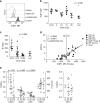
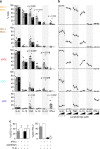
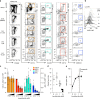
Ikaros family zinc finger 1 (IKZF1) is a haematopoietic transcription factor required for mammalian B-cell development. IKZF1 deficiency also reduces plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) numbers in mice, but its effects on human DC development are unknown. Here we show that heterozygous mutation of IKZF1 in human decreases pDC numbers and expands conventional DC1 (cDC1). Lenalidomide, a drug that induces proteosomal degradation of IKZF1, also decreases pDC numbers in vivo, and reduces the ratio of pDC/cDC1 differentiated from progenitor cells in vitro in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, non-classical monocytes are reduced by IKZF1 deficiency in vivo VSports手机版. DC and monocytes from patients with IKZF1 deficiency or lenalidomide-treated cultures secrete less IFN-α, TNF and IL-12. These results indicate that human DC development and function are regulated by IKZF1, providing further insights into the consequences of IKZF1 mutation on immune function and the mechanism of immunomodulation by lenalidomide. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
"V体育平台登录" Figures

V体育2025版 - References
-
- Milner JD, Holland SM. The cup runneth over: lessons from the ever-expanding pool of primary immunodeficiency diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:635–648. doi: 10.1038/nri3493. - V体育平台登录 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Collin M, Bigley V, Haniffa M, Hambleton S. Human dendritic cell deficiency: the missing ID? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011;11:575–583. doi: 10.1038/nri3046. - "V体育官网入口" DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
VSports注册入口 - MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
Grants and funding
"VSports在线直播" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

