METTL3 regulates alternative splicing of MyD88 upon the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells
- PMID: 29502358
- PMCID: PMC5908103
- DOI: "V体育ios版" 10.1111/jcmm.13491
METTL3 regulates alternative splicing of MyD88 upon the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells
Abstract
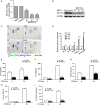
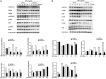
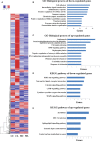
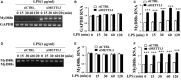
Dental pulp inflammation is a widespread public health problem caused by oral bacterial infections and can progress to pulp necrosis and periapical diseases. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a prevalent epitranscriptomic modification in mRNA. Previous studies have demonstrated that m6A methylation plays important roles in cell differentiation, embryonic development and stress responses. However, whether m6A modification affects dental pulp inflammation remains unknown. To address this issue, we investigated the expression of m6A and N6-adenosine methyltransferase (METTL3, METTL14) as well as demethylases (FTO, ALKBH5) and found that the levels of m6A and METTL3 were up-regulated in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Furthermore, we knocked down METTL3 and demonstrated that METTL3 depletion decreased the expression of inflammatory cytokines and the phosphorylation of IKKα/β, p65 and IκBα in the NF-κB signalling pathway as well as p38, ERK and JNK in the MAPK signalling pathway in LPS-induced HDPCs. The RNA sequencing analysis revealed that the vast number of genes affected by METTL3 depletion was associated with the inflammatory response. Previous research has shown that METTL3-dependent N6-adenosine methylation plays an important role in mRNA splicing. In this study, we found that METTL3 knockdown facilitated the expression of MyD88S, a splice variant of MyD88 that inhibits inflammatory cytokine production, suggesting that METTL3 might inhibit the LPS-induced inflammatory response of HDPCs by regulating alternative splicing of MyD88 VSports手机版. These data shed light on new findings in epitranscriptomic regulation of the inflammatory response and open new avenues for research into the molecular mechanisms of dental pulp inflammation. .
Keywords: METTL3; MyD88; N6-methyladenosine; alternative splicing; dental pulp inflammation; lipopolysaccharide V体育安卓版. .
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine. V体育ios版.
Figures

References
-
- Adams JM, Cory S. Modified nucleosides and bizarre 5’‐termini in mouse myeloma mRNA. Nature. 1975; 255: 28–33. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Furuichi Y, Morgan M, Shatkin AJ, et al Methylated, blocked 5 termini in HeLa cell mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975; 72: 1904–8. - V体育2025版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Geula S, Moshitch‐Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D, et al m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward differentiation. Science. 2015; 347: 1002–6. - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D, Moshitch‐Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, et al Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A‐seq. Nature. 2012; 485: 201–6. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育2025版)
"V体育平台登录" MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
VSports在线直播 - Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
VSports最新版本 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

