Long non-coding RNA and tumor hypoxia: new players ushered toward an old arena
- PMID: 28789687
- PMCID: PMC5547530
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-017-0358-4
Long non-coding RNA and tumor hypoxia: new players ushered toward an old arena (VSports手机版)
"V体育安卓版" Abstract
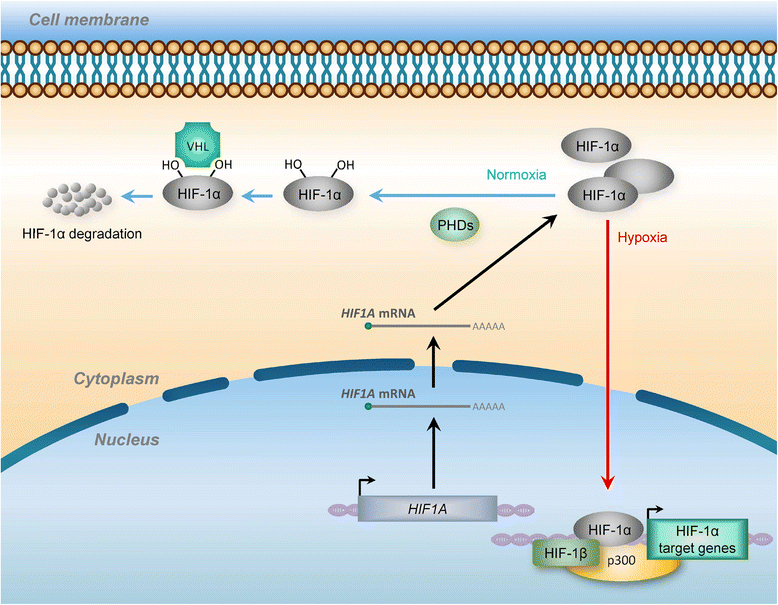
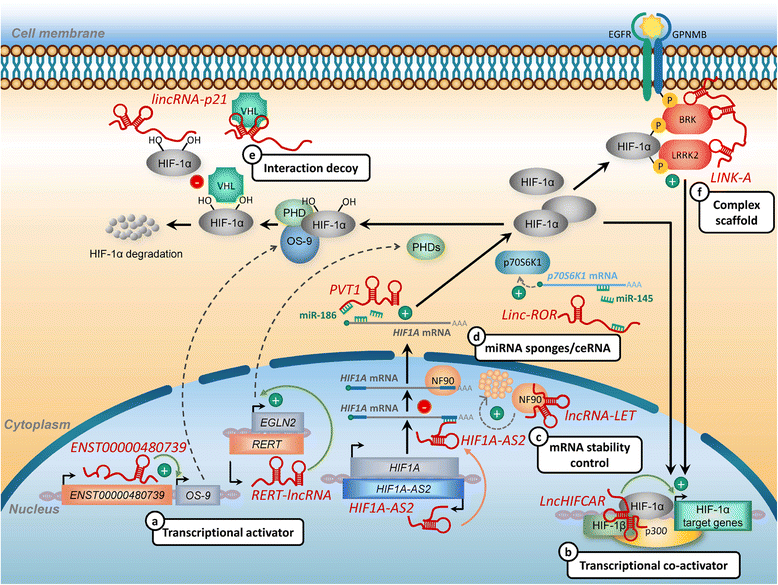
Hypoxia is a classic feature of the tumor microenvironment with a profound impact on cancer progression and therapeutic response. Activation of complex hypoxia pathways orchestrated by the transcription factor HIF (hypoxia-inducible factor) contributes to aggressive phenotypes and metastasis in numerous cancers. Over the past few decades, exponentially growing research indicated the importance of the non-coding genome in hypoxic tumor regions. Recently, key roles of long non coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in hypoxia-driven cancer progression have begun to emerge VSports手机版. These hypoxia-responsive lncRNAs (HRLs) play pivotal roles in regulating hypoxic gene expression at chromatic, transcriptional, and post-transcriptional levels by acting as effectors of the indirect response to HIF or direct modulators of the HIF-transcriptional cascade. Notably, the aberrant expression of HRLs significantly correlates with poor outcomes in cancer patients, showing promise for future utility as a tumor marker or therapeutic target. Here we address the latest advances made toward understanding the functional relevance of HRLs, the involvement of these transcripts in hypoxia response and the underlying action mechanisms, highlighting their specific roles in HIF-1 signaling regulation and hypoxia-associated malignant transformation. .
Keywords: Cancer; HIF-1α; HRL; Hypoxia; Hypoxia-responsive lncRNAs; Long non-coding RNA; Metastasis; lncRNA V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Semenza GL. Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Syst Biol Med. 2010;2:336–361. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, Liu L, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Wang D, Chen J, et al. Hypoxia induces genomic DNA demethylation through the activation of HIF-1alpha and transcriptional upregulation of MAT2A in hepatoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:1113–1123. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1010. - VSports在线直播 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH, et al. Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev. 1998;12:149–162. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.2.149. - DOI (V体育ios版) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports手机版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
V体育ios版 - Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

