H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance
- PMID: 28102845
- PMCID: PMC5386357
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.438 (VSports app下载)
H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance
Erratum in
-
"VSports在线直播" Correction: H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 27;15(8):628. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06793-5. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39191738 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
"VSports注册入口" Abstract
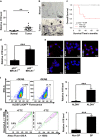
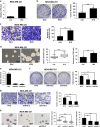
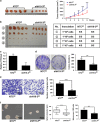
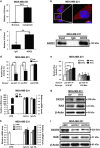
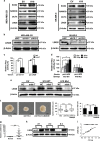
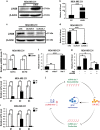
Long noncoding RNA-H19 (H19), an imprinted oncofetal gene, has a central role in carcinogenesis. Hitherto, the mechanism by which H19 regulates cancer stem cells, remains elusive. Here we show that breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) express high levels of H19, and ectopic overexpression of H19 significantly promotes breast cancer cell clonogenicity, migration and mammosphere-forming ability VSports手机版. Conversely, silencing of H19 represses these BCSC properties. In concordance, knockdown of H19 markedly inhibits tumor growth and suppresses tumorigenesis in nude mice. Mechanistically, we found that H19 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to sponge miRNA let-7, leading to an increase in expression of a let-7 target, the core pluripotency factor LIN28, which is enriched in BCSC populations and breast patient samples. Intriguingly, this gain of LIN28 expression can also feedback to reverse the H19 loss-mediated suppression of BCSC properties. Our data also reveal that LIN28 blocks mature let-7 production and, thereby, de-represses H19 expression in breast cancer cells. Appropriately, H19 and LIN28 expression exhibits strong correlations in primary breast carcinomas. Collectively, these findings reveal that lncRNA H19, miRNA let-7 and transcriptional factor LIN28 form a double-negative feedback loop, which has a critical role in the maintenance of BCSCs. Consequently, disrupting this pathway provides a novel therapeutic strategy for breast cancer. .
Conflict of interest statement (VSports app下载)
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
"VSports注册入口" Figures
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 87–108. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Filipova A, Seifrtova M, Mokry J, Dvorak J, Rezacova M, Filip S et al. Breast cancer and cancer stem cells: a mini-review. Tumori 2014; 100: 363–369. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Gianni L, Baselga J, Eiermann W, Porta VG, Semiglazov V, Lluch A et al. Phase III trial evaluating the addition of paclitaxel to doxorubicin followed by cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil, as adjuvant or primary systemic therapy: European Cooperative Trial in Operable Breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 2474–2481. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)Peto R Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)Davies C Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)Godwin J Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)Gray R Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG)Pan HC et al. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet 2012; 379: 432–444. - VSports app下载 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (V体育官网)
MeSH terms
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Grants and funding (V体育平台登录)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

