Impact of MicroRNA Levels, Target-Site Complementarity, and Cooperativity on Competing Endogenous RNA-Regulated Gene Expression
- PMID: 27871486
- PMCID: "V体育官网入口" PMC5101187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.027
Impact of MicroRNA Levels, Target-Site Complementarity, and Cooperativity on Competing Endogenous RNA-Regulated Gene Expression
Abstract
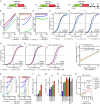
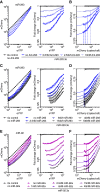
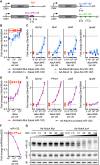
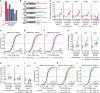
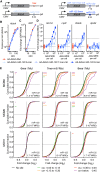
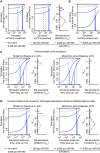
Expression changes of competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) have been proposed to influence microRNA (miRNA) activity and thereby regulate other transcripts containing miRNA-binding sites VSports手机版. Here, we find that although miRNA levels define the extent of repression, they have little effect on the magnitude of the ceRNA expression change required to observe derepression. Canonical 6-nt sites, which typically mediate modest repression, can nonetheless compete for miRNA binding, with potency ∼20% of that observed for canonical 8-nt sites. In aggregate, low-affinity/background sites also contribute to competition. Sites with extensive additional complementarity can appear as more potent, but only because they induce miRNA degradation. Cooperative binding of proximal sites for the same or different miRNAs does increase potency. These results provide quantitative insights into the stoichiometric relationship between miRNAs and target abundance, target-site spacing, and affinity requirements for ceRNA-mediated gene regulation, and the unusual circumstances in which ceRNA-mediated gene regulation might be observed. .
Keywords: base pair complementarity; competing endogenous RNA; cooperatively; gene regulation; miRNA; miRNA degradation; target abundance V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved V体育ios版. .
Figures


References (V体育ios版)
-
- Ala U., Karreth F.A., Bosia C., Pagnani A., Taulli R., Léopold V., Tay Y., Provero P., Zecchina R., Pandolfi P.P. Integrated transcriptional and competitive endogenous RNA networks are cross-regulated in permissive molecular environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:7154–7159. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–233. - PMC (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
"V体育官网" Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
VSports app下载 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

