Notch-1 Confers Chemoresistance in Lung Adenocarcinoma to Taxanes through AP-1/microRNA-451 Mediated Regulation of MDR-1
- PMID: 27727250
- PMCID: PMC5095685
- DOI: 10.1038/mtna.2016.82
Notch-1 Confers Chemoresistance in Lung Adenocarcinoma to Taxanes through AP-1/microRNA-451 Mediated Regulation of MDR-1
Abstract
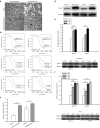
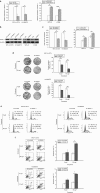
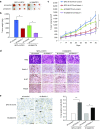
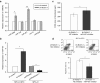
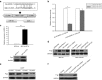
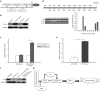
We previously demonstrated that expression of Notch-1 is associated with poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) patients. The aim of this study is to reveal whether Notch-1 was associated with Taxanes-resistant LAD and, the underlying mechanisms. We collected 39 patients of advanced LAD treated with Taxanes and found that positive Notch-1 expression is closely related to LAD lymph node metastasis, recurrence and poorer prognosis, and Notch-1 acts as an independent poor prognostic factor in LAD by multivariate analysis with Cox regression model. Then, by using the Docetaxel (DTX)-resistant LAD cell lines that we established previously, we found that Notch-1 contributes to resistance of LAD cells to DTX in vitro, and inhibition of Notch-1 sensitizes LAD to DTX in vivo. We further demonstrated that Notch-1 mediates chemoresistance response and strengthens proliferation capacity in LAD cells partially through negative regulation of miR-451 by transcription factor AP-1. Moreover, we found that MDR-1 is a direct target of miR-451 and influences chemoresistance of LAD cells. Taken together, our data revealed a novel Notch-1/AP-1/miR-451/MDR-1 signaling axis, and suggested a new therapeutic strategy of combining DTX with Notch inhibitors to treat DTX-resistant LAD. VSports手机版.
Figures
References
-
- Tan, N, Malek, M, Zha, J, Yue, P, Kassees, R, Berry, L et al. (2011). Navitoclax enhances the efficacy of taxanes in non-small cell lung cancer models. Clin Cancer Res 17: 1394–1404. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Avan, A, Maftouh, M, Avan, A, Tibaldi, C, Zucali, PA and Giovannetti, E (2014). SNPs in PI3K-PTEN-mTOR and brain metastases in NSCLC–letter. Clin Cancer Res 20: 3623–3624. - PubMed
-
- Cai, J, Fang, L, Huang, Y, Li, R, Yuan, J, Yang, Y et al. (2013). miR-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 73: 5402–5415. - PubMed
-
- Yu, T, Li, J, Yan, M, Liu, L, Lin, H, Zhao, F et al. (2014). MicroRNA-193a-3p and -5p suppress the metastasis of human non-small-cell lung cancer by downregulating the ERBB4/PIK3R3/mTOR/S6K2 signaling pathway. Oncogene 34: 413–423. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Wang, LH, Yang, JY, Yang, SN, Li, Y, Ping, GF, Hou, Y et al. (2014). Suppression of NF-κB signaling and P-glycoprotein function by gambogic acid synergistically potentiates adriamycin-induced apoptosis in lung cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 14: 91–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

