Spheroid Culture of Head and Neck Cancer Cells Reveals an Important Role of EGFR Signalling in Anchorage Independent Survival
- PMID: 27643613
- PMCID: PMC5028019 (VSports注册入口)
- DOI: V体育2025版 - 10.1371/journal.pone.0163149
Spheroid Culture of Head and Neck Cancer Cells Reveals an Important Role of EGFR Signalling in Anchorage Independent Survival
"V体育ios版" Abstract
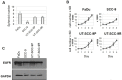
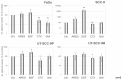
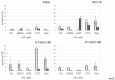
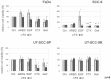
In solid tumours millions of cells are shed into the blood circulation each day. Only a subset of these circulating tumour cells (CTCs) survive, many of them presumable because of their potential to form multi-cellular clusters also named spheroids. Tumour cells within these spheroids are protected from anoikis, which allows them to metastasize to distant organs or re-seed at the primary site VSports手机版. We used spheroid cultures of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell lines as a model for such CTC clusters for determining the role of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in cluster formation ability and cell survival after detachment from the extra-cellular matrix. The HNSCC cell lines FaDu, SCC-9 and UT-SCC-9 (UT-SCC-9P) as well as its cetuximab (CTX)-resistant sub-clone (UT-SCC-9R) were forced to grow in an anchorage-independent manner by coating culture dishes with the anti-adhesive polymer poly-2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate (poly-HEMA). The extent of apoptosis, clonogenic survival and EGFR signalling under such culture conditions was evaluated. The potential of spheroid formation in suspension culture was found to be positively correlated with the proliferation rate of HNSCC cell lines as well as their basal EGFR expression levels. CTX and gefitinib blocked, whereas the addition of EGFR ligands promoted anchorage-independent cell survival and spheroid formation. Increased spheroid formation and growth were associated with persistent activation of EGFR and its downstream signalling component (MAPK/ERK). Importantly, HNSCC cells derived from spheroid cultures retained their clonogenic potential in the absence of cell-matrix contact. Addition of CTX under these conditions strongly inhibited colony formation in CTX-sensitive cell lines but not their resistant subclones. Altogether, EGFR activation was identified as crucial factor for anchorage-independent survival of HNSCC cells. Targeting EGFR in CTC cluster formation might represent an attractive anti-metastatic treatment approach in HNSCC. .
Conflict of interest statement (VSports注册入口)
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Butler TP, Gullino PM (1975) Quantitation of cell shedding into efferent blood of mammary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 35: 512–516. - PubMed
-
- Baccelli I, Schneeweiss A, Riethdorf S, Stenzinger A, Schillert A, et al. (2013) Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay. Nat Biotech 31: 539–544. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Baccelli I, Trumpp A (2012) The evolving concept of cancer and metastasis stem cells. J Cell Biol 198: 281–293. 10.1083/jcb.201202014 - "VSports在线直播" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tinhofer I, Saki M, Niehr F, Keilholz U, Budach V (2014) Cancer stem cell characteristics of circulating tumor cells. International Journal of Radiation Biology 90: 622–627. 10.3109/09553002.2014.886798 - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PubMed
-
- Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, Stopeck A, Matera J, et al. (2004) Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 351: 781–791. - PubMed
VSports在线直播 - MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育平台登录" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

