V体育官网 - BMI as a Modifiable Risk Factor for Type 2 Diabetes: Refining and Understanding Causal Estimates Using Mendelian Randomization
- PMID: 27402723
- PMCID: PMC5279886
- DOI: "V体育官网" 10.2337/db16-0418
"VSports" BMI as a Modifiable Risk Factor for Type 2 Diabetes: Refining and Understanding Causal Estimates Using Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
This study focused on resolving the relationship between BMI and type 2 diabetes. The availability of multiple variants associated with BMI offers a new chance to resolve the true causal effect of BMI on type 2 diabetes; however, the properties of these associations and their validity as genetic instruments need to be considered alongside established and new methods for undertaking Mendelian randomization (MR). We explore the potential for pleiotropic genetic variants to generate bias, revise existing estimates, and illustrate value in new analysis methods. A two-sample MR approach with 96 genetic variants was used with three different analysis methods, two of which (MR-Egger and the weighted median) have been developed specifically to address problems of invalid instrumental variables. We estimate an odds ratio for type 2 diabetes per unit increase in BMI (kg/m(2)) of between 1. 19 and 1 VSports手机版. 38, with the most stable estimate using all instruments and a weighted median approach (1. 26 [95% CI 1. 17, 1. 34]). TCF7L2(rs7903146) was identified as a complex effect or pleiotropic instrument, and removal of this variant resulted in convergence of causal effect estimates from different causal analysis methods. This indicated the potential for pleiotropy to affect estimates and differences in performance of alternative analytical methods. In a real type 2 diabetes-focused example, this study demonstrates the potential impact of invalid instruments on causal effect estimates and the potential for new approaches to mitigate the bias caused. .
© 2016 by the American Diabetes Association V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
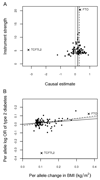
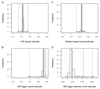
Comment in
-
The Next Step Forward Is to Take a Step Back.Diabetes. 2016 Oct;65(10):2824-5. doi: 10.2337/dbi16-0044. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27659224 No abstract available.
References
-
- Prospective Studies C. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. The Lancet. 373:1083–1096. - VSports最新版本 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holmes Michael V, Lange Leslie A, Palmer T, Lanktree Matthew B, North Kari E, Almoguera B, Buxbaum S, Chandrupatla Hareesh R, Elbers Clara C, Guo Y, Hoogeveen Ron C, et al. Causal Effects of Body Mass Index on Cardiometabolic Traits and Events: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. The American Journal of Human Genetics. 2014;94:198–208. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Human Molecular Genetics. 2014;23:R89–R98. - VSports app下载 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davey Smith G, Ebrahim S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? International Journal of Epidemiology. 2003;32:1–22. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JAC, Timpson N, Davey Smith G. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. 2008;27:1133–1163. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
"V体育官网" MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports - Actions
VSports最新版本 - Substances
Grants and funding (VSports在线直播)
- G0800270/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 19169/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N501906/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 100114/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- "VSports app下载" 100114/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- VSports最新版本 - MC_UU_12013/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00002/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- C18281/A19169/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 202802/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- "V体育官网入口" MC_UU_00002/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

