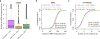m(6)A-LAIC-seq reveals the census and complexity of the m(6)A epitranscriptome
- PMID: 27376769
- PMCID: PMC5704921 (VSports在线直播)
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3898
m(6)A-LAIC-seq reveals the census and complexity of the m(6)A epitranscriptome (VSports)
Abstract
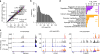
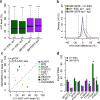
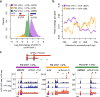
N(6)-Methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a widespread, reversible chemical modification of RNA molecules, implicated in many aspects of RNA metabolism. Little quantitative information exists as to either how many transcript copies of particular genes are m(6)A modified ('m(6)A levels') or the relationship of m(6)A modification(s) to alternative RNA isoforms. To deconvolute the m(6)A epitranscriptome, we developed m(6)A-level and isoform-characterization sequencing (m(6)A-LAIC-seq). We found that cells exhibit a broad range of nonstoichiometric m(6)A levels with cell-type specificity. At the level of isoform characterization, we discovered widespread differences in the use of tandem alternative polyadenylation (APA) sites by methylated and nonmethylated transcript isoforms of individual genes. Strikingly, there is a strong bias for methylated transcripts to be coupled with proximal APA sites, resulting in shortened 3' untranslated regions, while nonmethylated transcript isoforms tend to use distal APA sites VSports手机版. m(6)A-LAIC-seq yields a new perspective on transcriptome complexity and links APA usage to m(6)A modifications. .
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests
C. C. G. , Y. X. , B. M. , and J. W V体育安卓版. are in the process of filing a patent application for m6A-LAIC-seq.
Figures
Comment in
-
A glance at N(6)-methyladenosine in transcript isoforms.Nat Methods. 2016 Jul 28;13(8):624-5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3928. Nat Methods. 2016. PMID: 27467725 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fu Y, He C. Nucleic acid modifications with epigenetic significance. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2012;16:516–524. - V体育2025版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sibbritt T, Patel HR, Preiss T. Mapping and significance of the mRNA methylome. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013;4:397–422. - PubMed
-
- Klungland A, Dahl JA. Dynamic RNA modifications in disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014;26:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Pan T. N6-methyl-Adenosine modification in messenger and long non-coding RNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013;38:204–209. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
"V体育官网入口" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育安卓版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports最新版本)
Molecular Biology Databases (V体育平台登录)