V体育ios版 - MiRNA Transcriptome Profiling of Spheroid-Enriched Cells with Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Human Breast MCF-7 Cell Line
- PMID: 27019627
- PMCID: PMC4807162
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.12777
"VSports app下载" MiRNA Transcriptome Profiling of Spheroid-Enriched Cells with Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Human Breast MCF-7 Cell Line
VSports注册入口 - Abstract
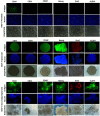
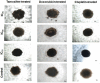
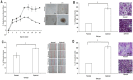
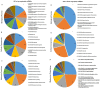
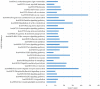
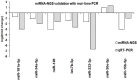
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide as most patients often suffer cancer relapse. The reason is often attributed to the presence of cancer stem cells (CSCs). Recent studies revealed that dysregulation of microRNA (miRNA) are closely linked to breast cancer recurrence and metastasis. However, no specific study has comprehensively characterised the CSC characteristic and miRNA transcriptome in spheroid-enriched breast cells. This study described the generation of spheroid MCF-7 cell in serum-free condition and the comprehensive characterisation for their CSC properties. Subsequently, miRNA expression differences between the spheroid-enriched CSC cells and their parental cells were evaluated using next generation sequencing (NGS). Our results showed that the MCF-7 spheroid cells were enriched with CSCs properties, indicated by the ability to self-renew, increased expression of CSCs markers, and increased resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Additionally, spheroid-enriched CSCs possessed greater cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and wound healing ability. A total of 134 significantly (p<0. 05) differentially expressed miRNAs were identified between spheroids and parental cells using miRNA-NGS. MiRNA-NGS analysis revealed 25 up-regulated and 109 down-regulated miRNAs which includes some miRNAs previously reported in the regulation of breast CSCs. A number of miRNAs (miR-4492, miR-4532, miR-381, miR-4508, miR-4448, miR-1296, and miR-365a) which have not been previously reported in breast cancer were found to show potential association with breast cancer chemoresistance and self-renewal capability VSports手机版. The gene ontology (GO) analysis showed that the predicted genes were enriched in the regulation of metabolic processes, gene expression, DNA binding, and hormone receptor binding. The corresponding pathway analyses inferred from the GO results were closely related to the function of signalling pathway, self-renewability, chemoresistance, tumorigenesis, cytoskeletal proteins, and metastasis in breast cancer. Based on these results, we proposed that certain miRNAs identified in this study could be used as new potential biomarkers for breast cancer stem cell diagnosis and targeted therapy. .
Keywords: MCF-7; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; miRNA transcriptome; next generation sequencing; spheroid culture. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared no competing interest exists.
Figures
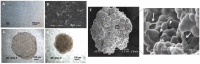
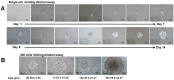
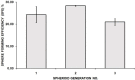
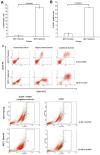
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. International Journal of Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis C, Howlader N, Cronin KA, Jemal A. Breast Cancer Incidence Rates in U.S. Women Are No Longer Declining. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2011;20:733–9. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Schiff R, Massarweh S, Shou J, Osborne CK. Breast Cancer Endocrine Resistance: How Growth Factor Signaling and Estrogen Receptor Coregulators Modulate Response. Clinical Cancer Research. 2003;9:447–54. - PubMed
-
- Setoguchi T, Taga T, Kondo T. Cancer Stem Cells Persist in Many Cancer Cell Lines. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:412–3. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
-
- Dean M. Cancer stem cells: Implications for cancer causation and therapy resistance. Discovery Medicine. 2005;5:278–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育平台登录" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

