4-(E)-{(p-tolylimino)-methylbenzene-1,2-diol}, 1 a novel resveratrol analog, differentially regulates estrogen receptors α and β in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 26970359
- PMCID: "V体育官网" PMC4860103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.03.003
"VSports注册入口" 4-(E)-{(p-tolylimino)-methylbenzene-1,2-diol}, 1 a novel resveratrol analog, differentially regulates estrogen receptors α and β in breast cancer cells
Abstract
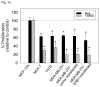
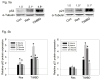
Breast cancer is a public health concern worldwide. Prolonged exposure to estrogens has been implicated in the development of breast neoplasms. Epidemiologic and experimental evidence suggest a chemopreventive role of phytoestrogens in breast cancers. Resveratrol, a naturally occurring phytoestrogen, has been shown to have potent anti-cancer properties. However, poor efficacy and bioavailability have prevented the use of resveratrol in clinics. In order to address these problems, we have synthesized a combinatorial library of azaresveratrol analogs and tested them for their ability to inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells. We have recently shown that 4-(E)-{(p-tolylimino)-methylbenzene-1,2-diol} (TIMBD), has better anti-cancer properties than resveratrol and any other resveratrol analog we have synthesized so far. The objective of this study was to investigate the regulation of estrogen receptors (ERs) α and β by TIMBD in breast cancer cell lines. We demonstrate that TIMBD significantly induces the mRNA and protein expression levels of ERβ and inhibits that of ERα. TIMBD inhibits mRNA and protein expression levels of oncogene c-Myc, and cell cycle protein cyclin D1, which are important regulators of cellular proliferation VSports手机版. TIMBD significantly induces protein expression levels of tumor suppressor genes p53 and p21 in MCF-7 cells. TIMBD inhibits c-Myc in an ERβ-dependent fashion in MCF-10A and ERβ1-transfected MDA-MB-231 cells, suggesting regulation of ERs as an important upstream mechanism of this analog. ERβ plays a partial role in inhibition of proliferation by TIMBD while ERα overexpression does not significantly affect TIMBD's inhibition. .
Keywords: Breast cancer inhibition; Estrogen receptors; Resveratrol analogs; TIMBD V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc V体育ios版. All rights reserved. .
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents in this article with respect to third party financial support, financial relationships, sources of revenue, sponsor interactions, patents or other affiliations.
Figures







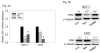
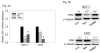





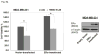
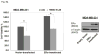
References
-
- Adlercreutz H. Phytoestrogens: epidemiology and a possible role in cancer protection. Environ Health Perspect. 1995;103:103–12. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
-
- Adlercreutz H. Phytoestrogens and breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;83:113–8. - PubMed
-
- Ursin G, Bernstein L, Pike MC. Breast Cancer. Cancer Surv. 1994;19–20:241–64. - PubMed
-
- Le Corre L, Chalabi N, Delort L, Bignon YJ, Bernard-Gallon DJ. Resveratrol and Breast Cancer Chemoprevention: Molecular Mechanisms. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005;49:462–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
Substances
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Grants and funding (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports注册入口 - Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

