Blocking c-Met-mediated PARP1 phosphorylation enhances anti-tumor effects of PARP inhibitors
- PMID: 26779812
- PMCID: PMC4754671
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4032
Blocking c-Met-mediated PARP1 phosphorylation enhances anti-tumor effects of PARP inhibitors
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Blocking c-Met-mediated PARP1 phosphorylation enhances anti-tumor effects of PARP inhibitors.Nat Med. 2016 Oct 6;22(10):1192. doi: 10.1038/nm1016-1192c. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27711065 No abstract available.
Abstract
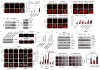
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have emerged as promising therapeutics for many diseases, including cancer, in clinical trials. One PARP inhibitor, olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca), was recently approved by the FDA to treat ovarian cancer with mutations in BRCA genes. BRCA1 and BRCA2 have essential roles in repairing DNA double-strand breaks, and a deficiency of BRCA proteins sensitizes cancer cells to PARP inhibition. Here we show that the receptor tyrosine kinase c-Met associates with and phosphorylates PARP1 at Tyr907 (PARP1 pTyr907 or pY907). PARP1 pY907 increases PARP1 enzymatic activity and reduces binding to a PARP inhibitor, thereby rendering cancer cells resistant to PARP inhibition VSports手机版. The combination of c-Met and PARP1 inhibitors synergized to suppress the growth of breast cancer cells in vitro and xenograft tumor models, and we observed similar synergistic effects in a lung cancer xenograft tumor model. These results suggest that the abundance of PARP1 pY907 may predict tumor resistance to PARP inhibitors, and that treatment with a combination of c-Met and PARP inhibitors may benefit patients whose tumors show high c-Met expression and who do not respond to PARP inhibition alone. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


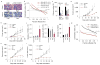
References
-
- Bryant HE, et al. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature. 2005;434:913–917. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Farmer H, et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature. 2005;434:917–921. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Irani K, et al. Mitogenic signaling mediated by oxidants in Ras-transformed fibroblasts. Science. 1997;275:1649–1652. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:579–591. - PubMed
"VSports app下载" Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances (VSports)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Grants and funding (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育官网入口)
"VSports在线直播" Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous (VSports app下载)

