Antiatherosclerotic Effects of 1-Methylnicotinamide in Apolipoprotein E/Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Deficient Mice: A Comparison with Nicotinic Acid
- PMID: 26631491
- PMCID: PMC6047228
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.115.228643
Antiatherosclerotic Effects of 1-Methylnicotinamide in Apolipoprotein E/Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Deficient Mice: A Comparison with Nicotinic Acid
Abstract
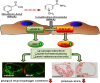
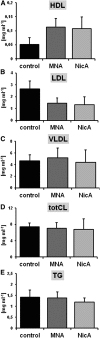
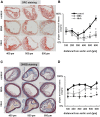
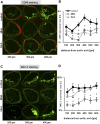
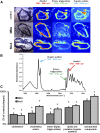
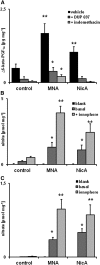
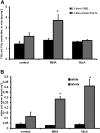
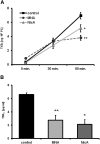
1-Methylnicotinamide (MNA), the major endogenous metabolite of nicotinic acid (NicA), may partially contribute to the vasoprotective properties of NicA. Here we compared the antiatherosclerotic effects of MNA and NicA in apolipoprotein E (ApoE)/low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR)-deficient mice. ApoE/LDLR(-/-) mice were treated with MNA or NicA (100 mg/kg). Plaque size, macrophages, and cholesterol content in the brachiocephalic artery, endothelial function in the aorta, systemic inflammation, platelet activation, as well as the concentration of MNA and its metabolites in plasma and urine were measured. MNA and NicA reduced atherosclerotic plaque area, plaque inflammation, and cholesterol content in the brachiocephalic artery VSports手机版. The antiatherosclerotic actions of MNA and NicA were associated with improved endothelial function, as evidenced by a higher concentration of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 α and nitrite/nitrate in the aortic ring effluent, inhibition of platelets (blunted thromboxane B2 generation), and inhibition of systemic inflammation (lower plasma concentration of serum amyloid P, haptoglobin). NicA treatment resulted in an approximately 2-fold higher concentration of MNA and its metabolites in urine and a 4-fold higher nicotinamide/MNA ratio in plasma, compared with MNA treatment. In summary; MNA displays pronounced antiatherosclerotic action in ApoE/LDLR(-/-) mice, an effect associated with an improvement in prostacyclin- and nitric oxide-dependent endothelial function, inhibition of platelet activation, inhibition of inflammatory burden in plaques, and diminished systemic inflammation. Despite substantially higher MNA availability after NicA treatment, compared with an equivalent dose of MNA, the antiatherosclerotic effect of NicA was not stronger. We suggest that detrimental effects of NicA or its metabolites other than MNA may limit beneficial effects of NicA-derived MNA. .
Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. V体育安卓版.
Figures
References
-
- Aksoy S, Szumlanski CL, Weinshilboum RM. (1994) Human liver nicotinamide N-methyltransferase. cDNA cloning, expression, and biochemical characterization. J Biol Chem 269:14835–14840. - PubMed
-
- Bartuś M, Łomnicka M, Kostogrys RB, Kaźmierczak P, Watała C, Słominska EM, Smoleński RT, Pisulewski PM, Adamus J, Gebicki J, et al. (2008) 1-Methylnicotinamide (MNA) prevents endothelial dysfunction in hypertriglyceridemic and diabetic rats. Pharmacol Rep 60:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Belenky P, Bogan KL, Brenner C. (2007) NAD+ metabolism in health and disease. Trends Biochem Sci 32:12–19. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Bryniarski K, Biedron R, Jakubowski A, Chlopicki S, Marcinkiewicz J. (2008) Anti-inflammatory effect of 1-methylnicotinamide in contact hypersensitivity to oxazolone in mice; involvement of prostacyclin. Eur J Pharmacol 578:332–338. - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
VSports注册入口 - Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports app下载" Other Literature Sources
VSports - Medical
Miscellaneous

