Generation, Release, and Uptake of the NAD Precursor Nicotinic Acid Riboside by Human Cells
- PMID: 26385918
- PMCID: PMC4646395
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.664458
Generation, Release, and Uptake of the NAD Precursor Nicotinic Acid Riboside by Human Cells
"VSports手机版" Abstract
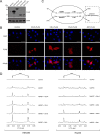
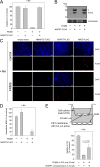
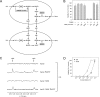
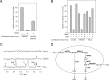
NAD is essential for cellular metabolism and has a key role in various signaling pathways in human cells. To ensure proper control of vital reactions, NAD must be permanently resynthesized. Nicotinamide and nicotinic acid as well as nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinic acid riboside (NAR) are the major precursors for NAD biosynthesis in humans. In this study, we explored whether the ribosides NR and NAR can be generated in human cells. We demonstrate that purified, recombinant human cytosolic 5'-nucleotidases (5'-NTs) CN-II and CN-III, but not CN-IA, can dephosphorylate the mononucleotides nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NAMN) and thus catalyze NR and NAR formation in vitro. Similar to their counterpart from yeast, Sdt1, the human 5'-NTs require high (millimolar) concentrations of nicotinamide mononucleotide or NAMN for efficient catalysis. Overexpression of FLAG-tagged CN-II and CN-III in HEK293 and HepG2 cells resulted in the formation and release of NAR. However, NAR accumulation in the culture medium of these cells was only detectable under conditions that led to increased NAMN production from nicotinic acid. The amount of NAR released from cells engineered for increased NAMN production was sufficient to maintain viability of surrounding cells unable to use any other NAD precursor. Moreover, we found that untransfected HeLa cells produce and release sufficient amounts of NAR and NR under normal culture conditions VSports手机版. Collectively, our results indicate that cytosolic 5'-NTs participate in the conversion of NAD precursors and establish NR and NAR as integral constituents of human NAD metabolism. In addition, they point to the possibility that different cell types might facilitate each other's NAD supply by providing alternative precursors. .
Keywords: 5′-nucleotidase; NAD biosynthesis; molecular cell biology; nicotinamide; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD); nicotinic acid; nicotinic acid riboside; nucleoside/nucleotide metabolism V体育安卓版. .
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc V体育ios版. .
Figures



References (VSports app下载)
-
- Hassa P. O., and Hottiger M. O. (2008) The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases. Front. Biosci. 13, 3046–3082 - PubMed
-
- Koch-Nolte F., Kernstock S., Mueller-Dieckmann C., Weiss M. S., and Haag F. (2008) Mammalian ADP-ribosyltransferases and ADP-ribosylhydrolases. Front. Biosci. 13, 6716–6729 - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网)
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
VSports app下载 - Research Materials

