Vagus nerve stimulation mitigates intrinsic cardiac neuronal and adverse myocyte remodeling postmyocardial infarction
- PMID: 26276818
- PMCID: PMC4666924
- DOI: V体育2025版 - 10.1152/ajpheart.00393.2015
VSports app下载 - Vagus nerve stimulation mitigates intrinsic cardiac neuronal and adverse myocyte remodeling postmyocardial infarction
Abstract
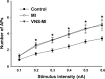
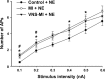
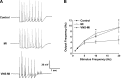
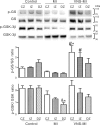
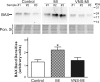
This paper aims to determine whether chronic vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) mitigates myocardial infarction (MI)-induced remodeling of the intrinsic cardiac nervous system (ICNS), along with the cardiac tissue it regulates. Guinea pigs underwent VNS implantation on the right cervical vagus. Two weeks later, MI was produced by ligating the ventral descending coronary artery. VNS stimulation started 7 days post-MI (20 Hz, 0. 9 ± 0. 2 mA, 14 s on, 48 s off; VNS-MI, n = 7) and was compared with time-matched MI animals with sham VNS (MI n = 7) vs. untreated controls (n = 8). Echocardiograms were performed before and at 90 days post-MI. At termination, IC neuronal intracellular voltage recordings were obtained from whole-mount neuronal plexuses. MI increased left ventricular end systolic volume (LVESV) 30% (P = 0. 027) and reduced LV ejection fraction (LVEF) 6. 5% (P < 0. 001) at 90 days post-MI compared with baseline. In the VNS-MI group, LVESV and LVEF did not differ from baseline. IC neurons showed depolarization of resting membrane potentials and increased input resistance in MI compared with VNS-MI and sham controls (P < 0. 05). Neuronal excitability and sensitivity to norepinephrine increased in MI and VNS-MI groups compared with controls (P < 0. 05). Synaptic efficacy, as determined by evoked responses to stimulating input axons, was reduced in VNS-MI compared with MI or controls (P < 0. 05). VNS induced changes in myocytes, consistent with enhanced glycogenolysis, and blunted the MI-induced increase in the proapoptotic Bcl-2-associated X protein (P < 0 VSports手机版. 05). VNS mitigates MI-induced remodeling of the ICNS, correspondingly preserving ventricular function via both neural and cardiomyocyte-dependent actions. .
Keywords: autonomic regulation therapy; guinea pig; intrinsic cardiac nervous system; myocardial infarction; vagus nerve stimulation V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society V体育ios版. .
Figures
References
-
- Ahonen A, Harkonen M, Juntunen J, Kormano M, Penttila A. Effects of myocardial infarction on adrenergic nerves of the rat heart muscle, a histochemical study. Acta Physiol Scand 93: 336–344, 1975. - PubMed
-
- Ajijola OA, Yagishita D, Patel KJ, Vaseghi M, Zhou W, Yamakawa K, So E, Lux RL, Mahajan A, Shivkumar K. Focal myocardial infarction induces global remodeling of cardiac sympathetic innervation: neural remodeling in a spatial context. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 305: H1031–H1040, 2013. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antoni ML, Boden H, Hoogslag GE, Ewe SH, Auger D, Holman ER, van der Wall EE, Schalij MJ, Bax JJ, Delgado V. Prevalence of dyssynchrony and relation with long-term outcome in patients after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 108: 1689–1696, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Ardell JL. Intrathoracic neuronal regulation of cardiac function In: Basic and Clinical Neurocardiology, edited by Armour JA, Ardell JL. New York: Oxford University Press, 2004, p. 118–152.
Publication types
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"VSports" MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

