V体育官网 - Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists for the prevention of shivering following general anaesthesia
- PMID: 26256531
- PMCID: PMC9221859
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011107.pub2 (V体育官网入口)
Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists for the prevention of shivering following general anaesthesia
Abstract
Background: Shivering after general anaesthesia is common. It is unpleasant but can also have adverse physiological effects. Alpha-2 (α-2) adrenergic agonist receptors, which can lead to reduced sympathetic activity and central regulation of vasoconstrictor tone, are a group of drugs that have been used to try to prevent postoperative shivering VSports手机版. .
Objectives: To assess the following: the effects of α-2 agonists on the prevention of shivering and subsequent complications after general anaesthesia in people undergoing surgery; the effects of α-2 agonists on the risk of inadvertent perioperative hypothermia; and whether any adverse effects are associated with these interventions. V体育安卓版.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and EMBASE on 13 June 2014 V体育ios版. Our search terms were relevant to the review question and limited to studies that assessed shivering or hypothermia. We also carried out searches of clinical trials registers, and forward and backward citation tracking. .
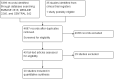
Selection criteria: We considered all randomized controlled trials, quasi-randomized studies, and cluster-randomized studies with adult participants undergoing surgery with general anaesthesia in which an α-2 agonist was compared with another α-2 agonist or a placebo for the prevention of shivering VSports最新版本. .
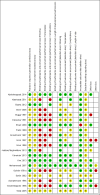
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data, consulting a third review author in the case of disagreements. We used standard Cochrane methodological procedures, including an assessment of risk of bias and use of GRADEpro software to interpret findings V体育平台登录. .
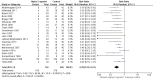
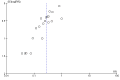
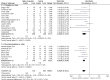
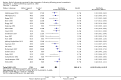
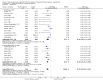
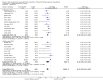
Main results: We included 20 studies with 1401 surgical participants comparing an α-2 agonist against a control VSports注册入口. Thirteen studies compared clonidine with a control, whilst seven compared dexmedetomidine with a control. The doses, methods, and time of administration varied between studies: three studies gave the drug orally or as an intravenous bolus preoperatively and nine intraoperatively; one study gave the drug as an infusion starting preoperatively and seven started at varying points from anaesthetic induction to the end of surgery. Whilst all the studies were described as randomized, many provided insufficient detail on methods used. We had anticipated that attempts would be made to reduce performance bias by blinding of personnel and participants, however this was detailed in only six of the papers. Similarly, in some studies detail was lacking on methods to reduce the risk of detection bias. We therefore downgraded the quality of evidence in our 'Summary of findings' table by one level for risk of bias using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach. All 20 included studies presented outcome data for postoperative shivering, and in meta-analysis α-2 agonists were shown to significantly reduce the risk of shivering (Mantel-Haenszel risk ratio 0. 28, 95% confidence interval 0. 18 to 0. 43, P value < 0. 0001). We found significant evidence of heterogeneity (I(2) = 80%) for this result that was not explained by sensitivity or subgroup analysis; we therefore downgraded the inconsistency of the evidence by one level. Although we did not feel that there were concerns with imprecision or indirectness of the data, we downgraded the quality of the evidence for the risk of publication bias following visual analysis of a funnel plot. Using GRADEpro, we rated the overall quality of the data for shivering as very low. Only one study reported the incidence of core hypothermia, whilst 12 studies measured core temperature. However, as the results for core temperature were reported in different styles, pooling the results was inappropriate. We found no studies with participant-reported outcomes such as experience of shivering or participant satisfaction. We found limited data for the outcomes of length of stay in the postanaesthetic care unit (three studies, 200 participants) and the following adverse effects: sedation (nine studies, 875 participants), bradycardia (eight studies, 716 participants), and hypotension (seven studies, 688 participants). Unpooled analysis suggested that sedation and bradycardia were significantly more common with dexmedetomidine than placebo, with all seven dexmedetomidine studies and none of the clonidine studies reporting statistically significantly higher levels of sedation as an adverse effect. .
Authors' conclusions: There is evidence that clonidine and dexmedetomidine can reduce postoperative shivering, but patients given dexmedetomidine may be more sedated V体育官网入口. However, our assessment of the quality of this evidence is very low. .
Conflict of interest statement (V体育安卓版)
Sharon R Lewis: None known.
Amanda Nicholson: From March to August 2011, AN worked for the Cardiff Research Consortium, which provided research and consultancy services to the pharmaceutical industry. Cardiff Research Consortium has no connection with AN's work with The Cochrane Collaboration VSports在线直播. AN's husband has small direct holdings in several drug and biotech companies as part of a wider balanced share portfolio. See Sources of support.
Andrew F Smith: None known.
Phil Alderson: None known.
Figures


Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011107
"V体育官网入口" References
References to studies included in this review
Abdelmageed 2014 {published data only}
-
- Abdelmageed WM, Al Taher WM. Intramuscular dexmedetomidine for prevention of shivering after general anesthesia in patients undergoing arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Ain‐Shams Journal of Anesthesiology 2014;07:156‐62.
Aldehayat 2011 {published data only}
-
- Aldehayat, G. Intraoperative dexmedetomidine administration at the end of surgery prevents post anesthetic shivering. Rawal Medical Journal 2011;36:274‐6.
Bajwa 2012 {published data only}
Bicer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bicer C, Esmaoglu A, Akin A, Boyaci A. Dexmedetomidine and meperidine prevent postanaesthetic shivering. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2006;23(2):149‐53. [PUBMED: 16426470] - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
Buggy 1997 {published data only}
-
- Buggy D, Higgins P, Moran C, O'Donovan F, McCarroll M. Clonidine at induction reduces shivering after general anaesthesia. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 1997;44:263‐7. [PUBMED: 9067044] - PubMed (VSports)
Delaunay 1991 {published data only}
-
- Delaunay L, Bonnet F, Duvaldestin P. Clonidine decreases postoperative oxygen consumption in patients recovering from general anaesthesia. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1991;67(4):397‐401. [PUBMED: 1931396] - V体育官网 - PubMed
Elvan 2008 {published data only}
-
- Elvan EG, Oc B, Uzun S, Karabulut E, Coskun F, Aypar U. Dexmedetomidine and postoperative shivering in patients undergoing elective abdominal hysterectomy. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2008;25:357‐64. [PUBMED: 18205960] - PubMed
Frank 1999 {published data only}
-
- Frank T, Thieme V, Olthoff D. Preoperative clonidine comedication within the scope of balanced inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane in oral surgery procedures. Anaesthesiologie und Reanimation 1999; Vol. 24, issue 3:65‐70. [PUBMED: 10472699] - PubMed
Grundmann 1997 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann U, Berg K, Stamminger U, Juckenhofel S, Wilhelm W. Comparison of pethidine and clonidine in the prevention of postoperative shivering. A prospective, randomised, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study. Anasthesiologie Intensivmedizin Notfallmedizin Schmerztherapie 1997;32(1):36‐42. [CN‐00199143] - PubMed
Horn 1997 {published data only}
-
- Horn EP, Werner C, Sessler DI, Steinfath M, Schulte Am Esch J. Late intraoperative clonidine administration prevents postanesthetic shivering after total intravenous or volatile anesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1997;84:613‐7. [PUBMED: 9052312] - PubMed
Horn 1998 {published data only}
-
- Horn EP, Standl T, Sessler DI, Knobelsdorff G, Buchs C, Schulte J. Physostigmine prevents postanesthetic shivering as does meperidine or clonidine. Anesthesiology 1998;88:108‐13. [PUBMED: 9447863] - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
Jabbary Moghaddam 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jabbary Moghaddam M, Ommi D, Mirkheshti A, Dabbagh A, Memary E, Sadeghi A, et al. Effects of clonidine premedication upon postoperative shivering and recovery time in patients with and without opium addiction after elective leg fracture surgeries. Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine 2013;2(3):107‐10. [PUBMED: 24244918] - PMC - PubMed
Karaman 2013 {published data only}
-
- Karaman S, Gunusen I, Ceylan MA, Karaman Y, Cetin EN, Derbent A, et al. Dexmedetomidine infusion prevents postoperative shivering in patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopic surgery. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2013;43:232‐7.
Kim 2013 {published data only}
Mohammadi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mohammadi SS, Seyedi M. Effects of oral clonidine in preventing postoperative shivering after general anesthesia. International Journal of Pharmacology 2007;3:441‐3.
Quintin 1991a {published data only}
-
- Quintin L, Viale JP, Annat G, Hoen JP, Butin E, Cottet‐Emard JM, et al. Oxygen uptake after major abdominal surgery: effect of clonidine. Anesthesiology 1991;74(2):236‐41. [PUBMED: 1990899] - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
Sahin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sahin T, Kilickan L, Canatay H, Baykara N, Toker K. The effect of clonidine on postoperative shivering in sevoflurane anaesthetized patients. Turk Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon 2002;30:203‐8.
Sumpelmann 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sumpelmann R, Brauer A, Krohn S, Schroder D, Strauss JM. Effects of intravenous clonidine on recovery and postanaesthetic analgesic requirements. Der Schmerz 1994;8(1):51‐6. [PUBMED: 18415455] - "V体育ios版" PubMed
Vanderstappen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Vanderstappen I, Vandermeersch E, Vanacker B, Mattheussen M, Herijgers P, Aken H. The effect of prophylactic clonidine on postoperative shivering. A large prospective double‐blind study. Anaesthesia 1996;51(4):351‐5. [PUBMED: 8686824] - PubMed
Yildiz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yildiz TS, Baykara N, Bozkurt N, Oysu DA, Solak M, Toker K. The effect of clonidine on shivering in low flow desflurane anaesthesia. Turk Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon Dernegi Dergisi 2005;33:29‐35.
References to studies excluded from this review
Apitzsch 2000 {published data only}
-
- Apitzsch H, Olthoff D, Thieme V, Vetter B, Wiegel M. The effects of perioperative continuous administration of mivazerol on early postoperative hemodynamics and plasma catecholamines after major surgery. Anasthesiologie Intensivmedizin Notfallmedizin Schmerztherapie 2000;35(8):515‐22. [PUBMED: 10992963] - PubMed
Arslan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Arslan G, Güreler C, Köse HE, Yurdakoç A, Günday I. Comparison of tramadol and clonidine in prophylaxis of shivering after general anaesthesia. European Society of Anaesthesiologists 2000;17:15.
Bakhamees 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bakhamees HS, El‐Halafawy YM, El‐Kerdawy HM, Gouda NM, Altemyatt S. Effects of dexmedetomidine in morbidly obese patients undergoing laparoscopic gastric bypass. Middle East Journal of Anesthesiology 2007;19:537‐51. [PUBMED: 18044282] - PubMed
Bernard 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bernard JM, Bourréli B, Homméril JL, Pinaud M. Effects of oral clonidine premedication and postoperative i.v. infusion on haemodynamic and adrenergic responses during recovery from anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1991;35(1):54‐9. [CN‐00074018] - PubMed
Bernard 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bernard JM, Fulgencio JP, Delaunay L, Bonnet F. Clonidine does not impair redistribution hypothermia after the induction of anesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1998;87(1):168‐72. [PUBMED: 9661568] - PubMed
Eberhart 2000 {published data only}
-
- Eberhart LH, Novatchkov N, Schricker T, Georgieff M, Baur CP. Clonidine compared to midazolam for intravenous premedication for ambulatory procedures. A controlled double blind study in ASA 1 patients. Anasthesiologie, Intensivmedizin, Notfallmedizin, Schmerztherapie 2000;35(6):388‐93. [PUBMED: 10900497] - PubMed
Gao 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gao GJ, Xu YY, Wang B, Lv HM, Yang WY, Shang Y. Feasibility of dexmedetomidine assisting sevoflurane for controlled hypotension in endoscopic sinus surgery. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army 2012;37(1):45‐8.
Hidalgo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hidalgo MP, Auzani JA, Rumpel LC, Moreira NL Jr, Cursino AW, Caumo W. The clinical effect of small oral clonidine doses on perioperative outcomes in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;100:795‐802. [PUBMED: 15728070] - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
Lee 2013 {published data only}
Mizobe 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mizobe T, Nakajima Y, Sunaguchi M, Ueno H, Sessler DI. Clonidine produces a dose‐dependent impairment of baroreflex‐mediated thermoregulatory responses to positive end‐expiratory pressure in anaesthetized humans. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2005;94(4):536‐41. [PUBMED: 15708868] - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
Onodera 2011 {published data only}
-
- Onodera Y, Yamagishi A, Kunisawa T, Kurosawa A, Takahata O, Iwasaki H. Postoperative analgesia of continuous intravenous fentanyl or dexmedetomidine for patients receiving anticoagulant therapy. Masui 2011;60(8):936‐40. [PUBMED: 21861419] - PubMed (VSports手机版)
Piper 2000 {published data only}
-
- Piper SN, Maleck WH, Boldt J, Suttner SW, Schmidt CC, Reich DG. A comparison of urapidil, clonidine, meperidine and placebo in preventing postanesthetic shivering. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2000;90(4):954‐7. [PUBMED: 10735806] - PubMed
Piper 2002 {published data only}
-
- Piper SN, Rohm KD, Maleck WH, Fent MT, Suttner SW, Boldt J. Dolasetron for preventing postanesthetic shivering. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2002;94(1):106‐11. [PUBMED: 11772810] - PubMed
Piper 2004 {published data only}
-
- Piper SN, Rohm KD, Suttner SW, Maleck WH, Kranke P, Boldt J. A comparison of nefopam and clonidine for the prevention of postanaesthetic shivering: a comparative, double‐blind and placebo‐controlled dose‐ranging study. Anaesthesia 2004;59(6):559‐64. [PUBMED: 15144295] - PubMed
Quintin 1991b {published data only}
-
- Quintin L, Roudot F, Roux C, Macquin I, Basmaciogullari A, Guyene T, et al. Effect of clonidine on the circulation and vasoactive hormones after aortic surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1991;66(1):108‐15. [PUBMED: 1997045] - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
Rohrbach 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rohrbach A, Jage J, Olthoff D. Intraoperative clonidine modulates sympathetic tone in the early postoperative period after remifentanil. A double blind, placebo‐controlled study. Acute Pain 1999;2:129‐38.
Wright 1990 {published data only}
-
- Wright PM, Carabine UA, McClune S, Orr DA, Moore J. Preanaesthetic medication with clonidine. British Journal of Surgery 1990;65:628‐32. [PUBMED: 2248839] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
IRCT138902083773N2 {published data only}
-
- IRCT138902083773N2. Evaluation of oral clonidine effects on prevention of post‐anesthesia shivering. "V体育ios版" http://www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?keyword=randomly&id=3773&fie... (accessed 13 June 2014).
Additional references
Alderson 2014
Alfonsi 2003
-
- Alfonsi P. Postanaesthetic shivering. Epidemiology, pathophysiology and approaches to prevention and management. Minerva Anestesiologica 2003;69(5):438‐42. [PUBMED: 12768180] - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
Biccard 2008
-
- Biccard BM, Goga S, Beurs J. Dexmedetomidine and cardiac protection for non‐cardiac surgery: a meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Anaesthesia 2008;63(1):4‐14. [PUBMED: 18086064] - PubMed
Brenner 2013
-
- Brenner GM, Stevens CW. Pharmacology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2013.
Buggy 2000
-
- Buggy DJ, Crossley AW. Thermoregulation, mild perioperative hypothermia and postanaesthetic shivering. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2000; Vol. 84, issue 5:615‐28. [PUBMED: 10844839] - PubMed
Campbell 2012
-
- Campbell G, Alderson P, Smith AF, Warttig S. Warming of intravenous and irrigation fluids for preventing inadvertent perioperative hypothermia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009891] - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Crossley 1994
-
- Crossley AW, Mahajan RP. The intensity of postoperative shivering is unrelated to axillary temperature. Anaesthesia 1994;49(3):205‐7. [PUBMED: 8147511] - PubMed
De Witte 2002
-
- Witte J, Sessler DI. Perioperative shivering: physiology and pharmacology. Anesthesiology 2002;96(2):467‐84. [PUBMED: 11818783] - "VSports手机版" PubMed
Eberhart 2005
-
- Eberhart LHJ, Döderlein F, Eisenhardt G, Kranke P, Sessler DI, Torossian A, et al. Independent risk factors for postoperative shivering. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;101(6):1849‐57. [PUBMED: 16301273] - PubMed
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group 2004‐2011. GRADEprofiler. Available at http://www.gradepro.org/gradepro/ (VSports), 2015.
Guyatt 2008
Harper 2008
-
- Harper CM, Andrzejowski JC, Alexander R. NICE and warm. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;101(3):293‐5. [PUBMED: 18710834] - "VSports" PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343:d5928. [PUBMED: 22008217] - PMC (V体育平台登录) - PubMed
Horosz 2013
-
- Horosz B, Malec‐Milewska M. Inadvertent intraoperative hypothermia. Anaesthesiology Intensive Therapy 2013;45(1):38‐43. [PUBMED: 23572308] - PubMed
Jalonen 1997
-
- Jalonen J, Hynynen M, Kuitunen A, Heikkila H, Perttila J, Salmenpera M, et al. Dexmedetomidine as an anesthetic adjunct in coronary artery bypass grafting. Anesthesiology 1997;86(2):331‐45. [PUBMED: 9054252] - PubMed
Kamibayashi 2000
-
- Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of alpha‐2‐adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology 2000;93(5):1345‐9. [PUBMED: 11046225] - VSports app下载 - PubMed
Kim 2013b
-
- Kim Y, Seo K. Optimal dose of prophylactic dexmedetomidine in preventing postoperative shivering. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2013;116:S‐45. - "VSports在线直播" PMC - PubMed
Kranke 2004
-
- Kranke P, Eberhart LH, Roewer N, Tramer MR. Single‐dose parenteral pharmacological interventions for the prevention of postoperative shivering: a quantitative systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2004;99(3):718‐27, table of contents. [PUBMED: 15333401] - "V体育官网" PubMed
Kurz 1995
-
- Kurz A, Sessler DI, Christensen R, Dechert M. Heat balance and distribution during the core‐temperature plateau in anesthetized humans. Anesthesiology 1995;83(3):491‐9. [PUBMED: 7661349] - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
Macario 1999
-
- Macario A, Weinger M, Carney S, Kim A. Which clinical anesthesia outcomes are important to avoid? The perspective of patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999;89(3):652‐8. [PUBMED: 10475299] - PubMed
Macario 1999a
-
- Macario A, Weinger M, Truong P, Lee M. Which clinical anesthesia outcomes are both common and important to avoid? The perspective of a panel of expert anesthesiologists. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999; Vol. 88, issue 5:1085‐91. [PUBMED: 10320175] - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
NICE Guideline CG65
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. The management of inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults. Clinical Guideline CG65. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG65/NiceGuidance/pdf/English (accessed 19 November 2013).
Nishina 2002
-
- Nishina K, Mikawa K, Uesugi T, Obara H, Maekawa M, Kamae I, et al. Efficacy of clonidine for prevention of perioperative myocardial ischemia: a critical appraisal and meta‐analysis of the literature. Anesthesiology 2002;96(2):323‐9. [PUBMED: 11818763] - PubMed
Park 2012
-
- Park SM, Mangat HS, Berger K, Rosengart AJ. Efficacy spectrum of antishivering medications: Meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Critical Care Medicine 2012;40(11):3070‐82. [PUBMED: 22890247 ] - PubMed
Piper 2000a
-
- No authors listed. A comparison of urapidil, clonidine, meperidine and placebo in preventing postanesthetic shivering: Retraction. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;112(5):1225. [PUBMED: 21451076] - PubMed
Piper 2002a
-
- No authors listed. Dolasetron for preventing postanesthetic shivering: Retraction. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011; Vol. 112, issue 5:1211. [PUBMED: 21451086] - PubMed
Piper 2004a
-
- No authors listed. A comparison of nefopam and clonidine for the prevention of postanaesthetic shivering: a comparative, double‐blind and placebo‐controlled dose‐ranging study: Retraction. Anaesthesia 2011;66(7):646. [PUBMED: 21826809] - VSports手机版 - PubMed
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Smith 2009
-
- Smith AF. In search of excellence in anesthesiology. Anesthesiology 2009;110:4‐5. [DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318190b263] - VSports最新版本 - DOI - PubMed
Smith 2011
-
- Smith AF, Glavin R, Greaves JD. Defining excellence in anaesthesia: the role of personal qualities and practice environment. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;106:38‐43. - PubMed
Urrútia 2011
-
- Urrútia G, Roqué i Figuls M, Campos JM, Paniagua P, Cibrian Sánchez S, Maestre L, et al. Active warming systems for preventing inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016] - "V体育平台登录" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Warttig 2014
-
- Warttig S, Alderson P, Campbell G, Smith AF. Interventions for treating inadvertent postoperative hypothermia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 11. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009892] - "V体育平台登录" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Warttig 2015
-
- Warttig S, Alderson P, Lewis SR, Smith AF. Intravenous nutrients for preventing inadvertent perioperative hypothermia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009906] - V体育ios版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wijeysundera 2009
-
- Wijeysundera DN, Bender JS, Beattie WS. Alpha‐2 adrenergic agonists for the prevention of cardiac complications among patients undergoing surgery. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004126.pub2] - V体育平台登录 - DOI - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
"V体育平台登录" Publication types
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
MeSH terms (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

