Improving survival by exploiting tumour dependence on stabilized mutant p53 for treatment
- PMID: 26009011
- PMCID: PMC4506213
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14430
"VSports最新版本" Improving survival by exploiting tumour dependence on stabilized mutant p53 for treatment
Erratum in (VSports在线直播)
-
Corrigendum: Improving survival by exploiting tumour dependence on stabilized mutant p53 for treatment.Nature. 2015 Nov 19;527(7578):398. doi: 10.1038/nature15720. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26416737 No abstract available.
Abstract
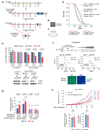
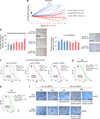
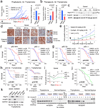
Missense mutations in p53 generate aberrant proteins with abrogated tumour suppressor functions that can also acquire oncogenic gain-of-function activities that promote malignant progression, invasion, metastasis and chemoresistance. Mutant p53 (mutp53) proteins undergo massive constitutive stabilization specifically in tumours, which is the key requisite for the acquisition of gain-of-functions activities. Although currently 11 million patients worldwide live with tumours expressing highly stabilized mutp53, it is unknown whether mutp53 is a therapeutic target in vivo. Here we use a novel mutp53 mouse model expressing an inactivatable R248Q hotspot mutation (floxQ) to show that tumours depend on sustained mutp53 expression. Upon tamoxifen-induced mutp53 ablation, allotransplanted and autochthonous tumours curb their growth, thus extending animal survival by 37%, and advanced tumours undergo apoptosis and tumour regression or stagnation. The HSP90/HDAC6 chaperone machinery, which is significantly upregulated in cancer compared with normal tissues, is a major determinant of mutp53 stabilization. We show that long-term HSP90 inhibition significantly extends the survival of mutp53 Q/- (R248Q allele) and H/H (R172H allele) mice by 59% and 48%, respectively, but not their corresponding p53(-/-) littermates. This mutp53-dependent drug effect occurs in H/H mice treated with 17DMAG+SAHA and in H/H and Q/- mice treated with the potent Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib. Notably, drug activity correlates with induction of mutp53 degradation, tumour apoptosis and prevention of T-cell lymphomagenesis. These proof-of-principle data identify mutp53 as an actionable cancer-specific drug target. VSports手机版.
Figures





References
-
- Doyle B, et al. p53 mutation and loss have different effects on tumourigenesis in a novel mouse model of pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. The Journal of pathology. 2010;222:129–137. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
-
- Hanel W, et al. Two hot spot mutant p53 mouse models display differential gain of function in tumorigenesis. Cell death and differentiation. 2013;20:898–909. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
-
- Lang GA, et al. Gain of function of a p53 hot spot mutation in a mouse model of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cell. 2004;119:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Morton JP, et al. Mutant p53 drives metastasis and overcomes growth arrest/senescence in pancreatic cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:246–251. - V体育平台登录 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olive KP, et al. Mutant p53 gain of function in two mouse models of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cell. 2004;119:847–860. - PubMed
Supplementary References
-
- Ventura A, et al. Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo. Nature. 2007;445:661–665. - PubMed
-
- Dobbelstein M, Moll U. Targeting tumour-supportive cellular machineries in anticancer drug development. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 2014;13:179–196. - PubMed
-
- Gorska M, et al. Geldanamycin and its derivatives as Hsp90 inhibitors. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2012;17:2269–2277. - PubMed
"VSports app下载" Publication types
VSports - MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Substances
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical (VSports最新版本)
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
"VSports" Miscellaneous

