"V体育2025版" Ovarian carcinoma CDK12 mutations misregulate expression of DNA repair genes via deficient formation and function of the Cdk12/CycK complex
- PMID: 25712099
- PMCID: PMC4357706
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv101
Ovarian carcinoma CDK12 mutations misregulate expression of DNA repair genes via deficient formation and function of the Cdk12/CycK complex
"VSports最新版本" Abstract
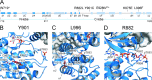
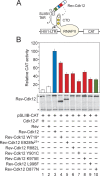
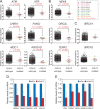
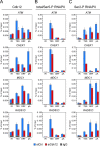
The Cdk12/CycK complex promotes expression of a subset of RNA polymerase II genes, including those of the DNA damage response. CDK12 is among only nine genes with recurrent somatic mutations in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. However, the influence of these mutations on the Cdk12/CycK complex and their link to cancerogenesis remain ill-defined. Here, we show that most mutations prevent formation of the Cdk12/CycK complex, rendering the kinase inactive. By examining the mutations within the Cdk12/CycK structure, we find that they likely provoke structural rearrangements detrimental to Cdk12 activation. Our mRNA expression analysis of the patient samples containing the CDK12 mutations reveals coordinated downregulation of genes critical to the homologous recombination DNA repair pathway. Moreover, we establish that the Cdk12/CycK complex occupies these genes and promotes phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II at Ser2 VSports手机版. Accordingly, we demonstrate that the mutant Cdk12 proteins fail to stimulate the faithful DNA double strand break repair via homologous recombination. Together, we provide the molecular basis of how mutated CDK12 ceases to function in ovarian carcinoma. We propose that CDK12 is a tumor suppressor of which the loss-of-function mutations may elicit defects in multiple DNA repair pathways, leading to genomic instability underlying the genesis of the cancer. .
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research V体育安卓版. .
Figures (VSports最新版本)

References
-
- Eick D., Geyer M. The RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) code. Chem. Rev. 2013;113:8456–8490. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Lenasi T., Barboric M. P-TEFb stimulates transcription elongation and pre-mRNA splicing through multilateral mechanisms. RNA Biol. 2010;7:145–150. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Bartkowiak B., Liu P., Phatnani H.P., Fuda N.J., Cooper J.J., Price D.H., Adelman K., Lis J.T., Greenleaf A.L. CDK12 is a transcription elongation-associated CTD kinase, the metazoan ortholog of yeast Ctk1. Genes Dev. 2010;24:2303–2316. - VSports注册入口 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases (VSports手机版)

