MiR-634 sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to paclitaxel and inhibits cell growth both in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25400759
- PMCID: PMC4230079
MiR-634 sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to paclitaxel and inhibits cell growth both in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
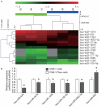
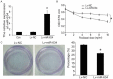
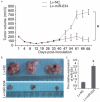
Resistance to chemotherapy is one of the key causal factors in cancer death and increasing evidence has revealed that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in chemoresistance in many kinds of human cancers VSports手机版. Paclitaxel has been used for treatment of advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC); however, treatment failure often occurs due to development of acquired paclitaxel resistance. In this study, based on miRNA microarray screening and qRT-PCR validation, we found six differentially expressed miRNAs in our induced paclitaxel-resistant NPC CNE-1/Taxol cells. Furthermore, we clarified the role of miR-634, most significantly downregulated in the paclitaxel-resistant CNE-1/Taxol, in regulating the paclitaxel sensitivity in NPC cells. We restored miR-634 expression in the CNE-1/Taxol cells by lentivirus infection, and found restoration of miR-634 re-sensitized the CNE-1/Taxol cells to paclitaxel in vitro by MTT assay and colony formation assay. In xenograft mouse model, we found that miR-634 inhibited tumor growth and enhanced paclitaxel sensitivity. Thus, our findings provide important information for the development of targeted gene therapy for reversing paclitaxel resistance in NPC. .
Keywords: Microarray; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; paclitaxel resistance; targeted therapy V体育安卓版. .
"VSports最新版本" Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:253–265. - PubMed
-
- Rowinsky EK. The development and clinical utility of the taxane class of antimicrotubule chemotherapy agents. Annu Rev Med. 1997;48:353–374. - VSports - PubMed
-
- He XY, Hu CS, Ying HM, Wu YR, Zhu GP, Liu TF. Paclitaxel with cisplatin in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267:773–778. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Leong SS, Wee J, Rajan S, Toh CK, Lim WT, Hee SW, Tay MH, Poon D, Tan EH. Triplet combination of gemcitabine, paclitaxel, and carboplatin followed by maintenance 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid in patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 2008;113:1332–1337. - V体育官网 - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- "VSports" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
