Human milk glycomics and gut microbial genomics in infant feces show a correlation between human milk oligosaccharides and gut microbiota: a proof-of-concept study
- PMID: 25300177
- PMCID: PMC4286166
- DOI: 10.1021/pr500759e (V体育2025版)
Human milk glycomics and gut microbial genomics in infant feces show a correlation between human milk oligosaccharides and gut microbiota: a proof-of-concept study (V体育2025版)
Abstract
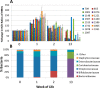
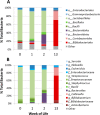
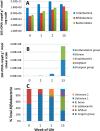
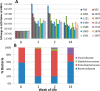
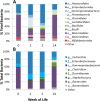
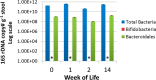
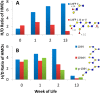
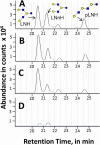
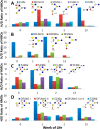
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) play a key role in shaping and maintaining a healthy infant gut microbiota. This article demonstrates the potential of combining recent advances in glycomics and genomics to correlate abundances of fecal microbes and fecal HMOs. Serial fecal specimens from two healthy breast-fed infants were analyzed by bacterial DNA sequencing to characterize the microbiota and by mass spectrometry to determine abundances of specific HMOs that passed through the intestinal tract without being consumed by the luminal bacteria. In both infants, the fecal bacterial population shifted from non-HMO-consuming microbes to HMO-consuming bacteria during the first few weeks of life VSports手机版. An initial rise in fecal HMOs corresponded with bacterial populations composed primarily of non-HMO-consuming Enterobacteriaceae and Staphylococcaeae. This was followed by decreases in fecal HMOs as the proportion of HMO-consuming Bacteroidaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae increased. Analysis of HMO structures with isomer differentiation revealed that HMO consumption is highly structure-specific, with unique isomers being consumed and others passing through the gut unaltered. These results represent a proof-of-concept and are consistent with the highly selective, prebiotic effect of HMOs in shaping the gut microbiota in the first weeks of life. The analysis of selective fecal bacterial substrates as a measure of alterations in the gut microbiota may be a potential marker of dysbiosis. .
Keywords: HMOs; Term infants; human milk; mass spectrometry; microbiota; oligosaccharides; prebiotic. V体育安卓版.
VSports在线直播 - Figures
References
-
- German J. B.; Dillard C. J.; Ward R. E. Bioactive components in milk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2002, 5, 653–8. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Ninonuevo M. R.; Park Y.; Yin H.; Zhang J.; Ward R. E.; Clowers B. H.; German J. B.; Freeman S. L.; Killeen K.; Grimm R.; Lebrilla C. B. A strategy for annotating the human milk glycome. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7471–80. - PubMed
-
- LoCascio R. G.; Ninonuevo M. R.; Freeman S. L.; Sela D. A.; Grimm R.; Lebrilla C. B.; Mills D. A.; German J. B. Glycoprofiling of bifidobacterial consumption of human milk oligosaccharides demonstrates strain specific, preferential consumption of small chain glycans secreted in early human lactation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8914–9. - VSports在线直播 - PubMed
-
- Yatsunenko T.; Rey F. E.; Manary M. J.; Trehan I.; Dominguez-Bello M. G.; Contreras M.; Magris M.; Hidalgo G.; Baldassano R. N.; Anokhin A. P.; Heath A. C.; Warner B.; Reeder J.; Kuczynski J.; Caporaso J. G.; Lozupone C. A.; Lauber C.; Clemente J. C.; Knights D.; Knight R.; Gordon J. I. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. - PMC - PubMed
V体育平台登录 - Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
V体育官网入口 - MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
Grants and funding (V体育2025版)
- HD059127/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P42ES02710/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States (V体育官网入口)
- GM049077/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES002710/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD061923/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD059127/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR027639/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01AT007079/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM049077/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027639/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD061923/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 ES002710/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT007079/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources (VSports手机版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育ios版" Medical

