Differential regulation of estrogen receptors α and β by 4-(E)-{(4-hydroxyphenylimino)-methylbenzene,1,2-diol}, a novel resveratrol analog
- PMID: 25242450
- PMCID: "V体育官网入口" PMC4195806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.09.015
Differential regulation of estrogen receptors α and β by 4-(E)-{(4-hydroxyphenylimino)-methylbenzene,1,2-diol}, a novel resveratrol analog
Abstract
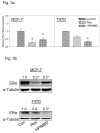
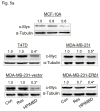
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of death among women in the United States. Estrogens have been implicated as major risk factors in the development of breast neoplasms. Recent epidemiologic studies have suggested a protective role of phytoestrogens in prevention of breast and other cancers. Resveratrol, a naturally occurring phytoestrogen found notably in red grapes, berries and peanuts, has been shown to possess potent anti-cancer properties. However, the poor efficacy of resveratrol has prevented its use in a clinical setting. In order to improve the efficacy of resveratrol, we have synthesized a small combinatorial library of azaresveratrol analogs and tested them for their ability to inhibit the growth of breast cancer cell lines. We have recently shown that one of the synthesized analogs, 4-(E)-{(4-hydroxyphenylimino)-methylbenzene,1,2-diol} (HPIMBD), has better anti-cancer properties than resveratrol. The objective of this study was to investigate the differential regulation of estrogen receptors (ERs) α and β as a potential mechanism of inhibition of breast cancer by HPIMBD VSports手机版. Estrogen receptors α and β have been shown to have opposing roles in cellular proliferation. Estrogen receptor α mediates the proliferative responses of estrogens while ERβ plays an anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic role. We demonstrate that HPIMBD significantly induces the expression of ERβ and inhibits the expression of ERα. HPIMBD also inhibits the protein expression levels of oncogene c-Myc and cell cycle protein cyclin D1, genes downstream to ERα and important regulators of cell cycle, and cellular proliferation. HPIMBD significantly induces protein expression levels of tumor suppressors p53 and p21 in MCF-7 cells. Additionally, HPIMBD inhibits c-Myc in an ERβ-dependent fashion in MCF-10A and ERβ1-transfected MDA-MB-231 cells, suggesting regulation of ERs as an important upstream mechanism of this novel compound. Molecular docking studies confirm higher affinity for binding of HPIMBD in the ERβ cavity. Thus, HPIMBD, a novel azaresveratrol analog may inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells by differentially modulating the expressions of ERs α and β. .
Keywords: Breast cancer; Estrogen receptors; Resveratrol; Resveratrol analogs V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd V体育ios版. All rights reserved. .
V体育ios版 - Figures
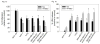
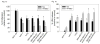
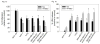
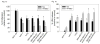
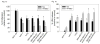
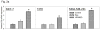
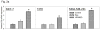
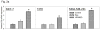




References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Shinohara MM, Tozbikian G, Wolfe JT, Shin SJ, Mies C, Elenitsas R. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma with clear cell features. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:753–757. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:52–62. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Singh B, Bhat HK. Superoxide dismutase 3 is induced by antioxidants, inhibits oxidative DNA damage and is associated with inhibition of estrogen-induced breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:2601–2610. - V体育官网入口 - PMC - PubMed
"V体育官网" Publication types
- VSports - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
"V体育平台登录" Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育官网)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials (VSports手机版)
Miscellaneous

