Epidemiology of acute respiratory infections in children in Guangzhou: a three-year study
- PMID: 24797911
- PMCID: PMC4010508
- DOI: VSports最新版本 - 10.1371/journal.pone.0096674
Epidemiology of acute respiratory infections in children in Guangzhou: a three-year study (VSports app下载)
Abstract (VSports手机版)
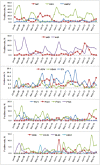
Acute Respiratory Infections (ARI) are some of the most common human diseases worldwide. However, they have a complex and diverse etiology, and the characteristics of the pathogens involved in respiratory infections in developing countries are not well understood. In this work, we analyzed the characteristics of 17 common respiratory pathogens in children (≤14 years old) with ARI in Guangzhou, southern China over a 3-year period using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Pathogens were identified in 2361/4242 (55. 7%) patients, and the positivity rate varied seasonally. Ten of the 17 pathogens investigated showed positivity rates of more than 5%. The most frequently detected pathogens were respiratory syncytial virus (768/2361, 32. 5%), influenza A virus (428/2361, 18. 1%), enterovirus (138/2361, 13. 3%), Mycoplasma pneumoniae (267/2361, 11. 3%) and adenovirus (213/2361, 9. 0%). Co-pathogens were common and found in 503 of 2361 (21. 3%) positive samples. When ranked according to frequency of occurrence, the pattern of co-pathogens was similar to that of the primary pathogens, with the exception of human bocavirus, human coronavirus and human metapneumovirus. Significant differences were found in age prevalence in 10 of the 17 pathogens (p≤0. 009): four basic patterns were observed, A: detection rates increased with age, B: detection rates declined with age, C: the detection rate showed distinct peaks or D: numbers of patients were too low to detect a trend or showed no significant difference among age groups (p>0. 05) VSports手机版. These data will be useful for planning vaccine research and control strategies and for studies predicting pathogen prevalence. .
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



"V体育官网入口" References
-
- Berman S (1991) Epidemiology of acute respiratory infections in children of developing countries. Rev Infect Dis 13: S454–462. - VSports - PubMed
-
- Monto AS (1989) Acute respiratory infection in children of developing countries: challenge of the 1990s. Rev Infect Dis 11(3): 498–505. - VSports在线直播 - PubMed
-
- Williams BG, Gouws E, Boschi-Pinto C, Bryce J, Dye C (2002) Estimates of world-wide distribution of child deaths from acute respiratory infections. Lancet Infect Dis 2(1): 25–32. - PubMed
-
- Mahony JB (2008) Detection of respiratory viruses by molecular methods. Clin Microbiol Rev 21(4): 716–747. - VSports手机版 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

