"V体育2025版" Differential effects of sorafenib on liver versus tumor fibrosis mediated by stromal-derived factor 1 alpha/C-X-C receptor type 4 axis and myeloid differentiation antigen-positive myeloid cell infiltration in mice
- PMID: 24242874
- PMCID: PMC3966948
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.26790
Differential effects of sorafenib on liver versus tumor fibrosis mediated by stromal-derived factor 1 alpha/C-X-C receptor type 4 axis and myeloid differentiation antigen-positive myeloid cell infiltration in mice
Abstract
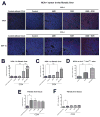
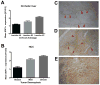
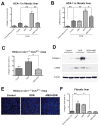
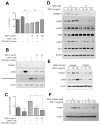
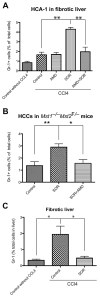
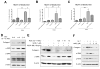
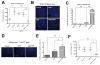
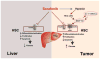
Sorafenib--a broad kinase inhibitor--is a standard therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has been shown to exert antifibrotic effects in liver cirrhosis, a precursor of HCC. However, the effects of sorafenib on tumor desmoplasia--and its consequences on treatment resistance--remain unknown. We demonstrate that sorafenib has differential effects on tumor fibrosis versus liver fibrosis in orthotopic models of HCC in mice VSports手机版. Sorafenib intensifies tumor hypoxia, which increases stromal-derived factor 1 alpha (SDF-1α) expression in cancer and stromal cells and, subsequently, myeloid differentiation antigen-positive (Gr-1(+)) myeloid cell infiltration. The SDF-1α/C-X-C receptor type 4 (CXCR4) pathway directly promotes hepatic stellate cell (HSC) differentiation and activation through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. This is consistent with the association between SDF-1α expression with fibrotic septa in cirrhotic liver tissues as well as with desmoplastic regions of human HCC samples. We demonstrate that after treatment with sorafenib, SDF-1α increased the survival of HSCs and their alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen I expression, thus increasing tumor fibrosis. Finally, we show that Gr-1(+) myeloid cells mediate HSC differentiation and activation in a paracrine manner. CXCR4 inhibition, using AMD3100 in combination with sorafenib treatment, prevents the increase in tumor fibrosis--despite persistently elevated hypoxia--in part by reducing Gr-1(+) myeloid cell infiltration and inhibits HCC growth. Similarly, antibody blockade of Gr-1 reduces tumor fibrosis and inhibits HCC growth when combined with sorafenib treatment. .
Conclusion: Blocking SDF-1α/CXCR4 or Gr-1(+) myeloid cell infiltration may reduce hypoxia-mediated HCC desmoplasia and increase the efficacy of sorafenib treatment. V体育安卓版.
© 2014 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases V体育ios版. .
Figures
"VSports在线直播" References
-
- Hui CK, Leung N, Shek TW, Yao H, Lee WK, Lai JY, Lai ST, et al. Sustained disease remission after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion is associated with reduction in fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis B Chinese patients. Hepatology. 2007;46:690–698. - PubMed
-
- Luedde T, Schwabe RF. NF-kappaB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:108–118. - V体育平台登录 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:425–436. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7099–7109. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
Publication types
VSports注册入口 - MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Grants and funding (V体育平台登录)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
