VSports app下载 - Hesperetin alleviates the inhibitory effects of high glucose on the osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- PMID: 23840726
- PMCID: PMC3696082
- DOI: V体育官网 - 10.1371/journal.pone.0067504
"V体育2025版" Hesperetin alleviates the inhibitory effects of high glucose on the osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
Abstract
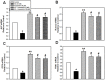
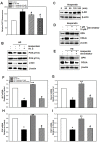
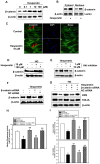
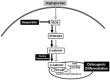
Hesperetin (3',5,7-trihydroxy-4-methoxyflavanone) is a metabolite of hesperidin (hesperetin-7-O-rutinoside), which belongs to the flavanone subgroup and is found mainly in citrus fruits. Hesperetin has been reported to be an effective osteoinductive compound in various in vivo and in vitro models. However, how hesperetin effects osteogenic differentiation is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the capacity of hesperetin to stimulate the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) and to relieve the anti-osteogenic effect of high glucose. Osteogenesis of PDLSCs was assessed by measurement of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and evaluation of the mRNA expression of ALP, runt-related gene 2 (Runx2), osterix (OSX), and FRA1 as osteogenic transcription factors, as well as assessment of protein expression of osteopontin (OPN) and collagen type IA (COLIA). When PDLSCs were exposed to a high concentration (30 mM) of glucose, osteogenic activity decreased compared to control cells. Hesperetin significantly increased ALP activity at doses of 1, 10, and 100 µM. Pretreatment of cells with hesperetin alleviated the high-glucose-induced suppression of the osteogenic activity of PDLSCs. Hesperetin scavenged intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced under high glucose condition. Furthermore, hesperetin increased the activity of the PI3K/Akt and β-catenin pathways. Consistent with this, blockage of Akt or β-catenin diminished the protective effect of hesperetin against high glucose-inhibited osteogenic differentiation. Collectively, our results suggest that hesperetin alleviates the high glucose-mediated suppression of osteogenic differentiation in PDLSCs by regulating ROS levels and the PI3K/Akt and β-catenin signaling pathways. VSports手机版.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM, Batouli S, et al. (2004) Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet 364: 149–155. - PubMed
-
- Singhatanadgit W, Donos N, Olsen I (2009) Isolation and characterization of stem cell clones from adult human ligament. Tissue Eng A 15: 2625–2636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Substances
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials (V体育ios版)

