Scientific benchmarks for guiding macromolecular energy function improvement
- PMID: 23422428
- PMCID: "V体育安卓版" PMC3724755
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394292-0.00006-0
Scientific benchmarks for guiding macromolecular energy function improvement
Abstract
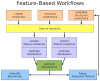
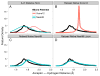
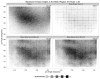
Accurate energy functions are critical to macromolecular modeling and design. We describe new tools for identifying inaccuracies in energy functions and guiding their improvement, and illustrate the application of these tools to the improvement of the Rosetta energy function VSports手机版. The feature analysis tool identifies discrepancies between structures deposited in the PDB and low-energy structures generated by Rosetta; these likely arise from inaccuracies in the energy function. The optE tool optimizes the weights on the different components of the energy function by maximizing the recapitulation of a wide range of experimental observations. We use the tools to examine three proposed modifications to the Rosetta energy function: improving the unfolded state energy model (reference energies), using bicubic spline interpolation to generate knowledge-based torisonal potentials, and incorporating the recently developed Dunbrack 2010 rotamer library (Shapovalov & Dunbrack, 2011). .
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc V体育安卓版. All rights reserved. .
Figures
References
-
- Bower MJ, Cohen FE, Dunbrack RL., Jr Prediction of protein side-chain rotamers from a backbone-dependent rotamer library: a new homology modeling tool. J Mol Biol. 1997;267:1268–1282. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
-
- Chen HM, Liu BF, Huang HL, Hwang SF, Ho SY. Sodock: Swarm optimization for highly flexible protein-ligand docking. J Comp Chem. 2007;28:612–623. - PubMed
-
- Das R, Baker D. Macromolecular modeling with rosetta. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:363–82. - PubMed
VSports - Publication types
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions

