p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs
- PMID: 23236145
- PMCID: PMC3538199
- DOI: VSports - 10.1073/pnas.1216922110
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs
V体育安卓版 - Abstract
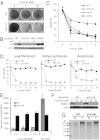
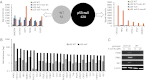
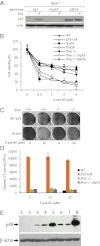
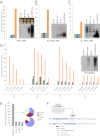
Large parts of mammalian genomes are transcriptionally inactive and enriched with various classes of interspersed and tandem repeats. Here we show that the tumor suppressor protein p53 cooperates with DNA methylation to maintain silencing of a large portion of the mouse genome. Massive transcription of major classes of short, interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) B1 and B2, both strands of near-centromeric satellite DNAs consisting of tandem repeats, and multiple species of noncoding RNAs was observed in p53-deficient but not in p53 wild-type mouse fibroblasts treated with the DNA demethylating agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine. The abundance of these transcripts exceeded the level of β-actin mRNA by more than 150-fold. Accumulation of these transcripts, which are capable of forming double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), was accompanied by a strong, endogenous, apoptosis-inducing type I IFN response. This phenomenon, which we named "TRAIN" (for "transcription of repeats activates interferon"), was observed in spontaneous tumors in two models of cancer-prone mice, presumably reflecting naturally occurring DNA hypomethylation and p53 inactivation in cancer. These observations suggest that p53 and IFN cooperate to prevent accumulation of cells with activated repeats and provide a plausible explanation for the deregulation of IFN function frequently seen in tumors. Overall, this work reveals roles for p53 and IFN that are key for genetic stability and therefore relevant to both tumorigenesis and the evolution of species VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement (VSports app下载)
Conflict of interest statement: A. V. G. is a consultant and shareholder of Tartis, Inc. , a biotech company that provided funding for this work V体育安卓版.
Figures
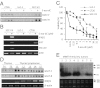
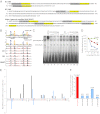
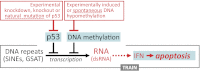
VSports app下载 - Comment in
-
p53 and DNA methylation suppress the TRAIN to cell death.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 1;12(1):9-10. doi: 10.4161/cc.23324. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23255100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
VSports最新版本 - References
-
- Makałowski W. Genomic scrap yard: How genomes utilize all that junk. Gene. 2000;259(1-2):61–67. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
-
- Kramerov DA, Vassetzky NS. SINEs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2(6):772–786. - PubMed
-
- Smit AF. Interspersed repeats and other mementos of transposable elements in mammalian genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9(6):657–663. - PubMed
-
- Ostertag EM, Kazazian HH., Jr Biology of mammalian L1 retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet. 2001;35:501–538. - PubMed
-
- Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W. The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature. 1994;371(6494):215–220. - V体育ios版 - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育ios版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

