High-dose resveratrol supplementation in obese men: an investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition
- PMID: 23193181
- PMCID: PMC3609591
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0975 (V体育安卓版)
VSports在线直播 - High-dose resveratrol supplementation in obese men: an investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition
VSports手机版 - Abstract
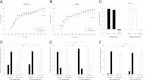
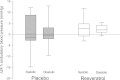
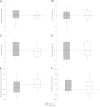
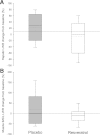
Obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia constitute risk factors for morbidity and premature mortality. Based on animal and in vitro studies, resveratrol reverts these risk factors via stimulation of silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1), but data in human subjects are scarce. The objective of this study was to examine the metabolic effects of high-dose resveratrol in obese human subjects VSports手机版. In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, and parallel-group design, 24 obese but otherwise healthy men were randomly assigned to 4 weeks of resveratrol or placebo treatment. Extensive metabolic examinations including assessment of glucose turnover and insulin sensitivity (hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp) were performed before and after the treatment. Insulin sensitivity, the primary outcome measure, deteriorated insignificantly in both groups. Endogenous glucose production and the turnover and oxidation rates of glucose remained unchanged. Resveratrol supplementation also had no effect on blood pressure; resting energy expenditure; oxidation rates of lipid; ectopic or visceral fat content; or inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers. The lack of effect disagrees with persuasive data obtained from rodent models and raises doubt about the justification of resveratrol as a human nutritional supplement in metabolic disorders. .
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials. gov NCT01150955. V体育安卓版.
Figures
Comment in
-
VSports注册入口 - Exploring the promise of resveratrol: where do we go from here?Diabetes. 2013 Apr;62(4):1022-3. doi: 10.2337/db12-1788. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23520278 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References (V体育安卓版)
-
- World Health Organization. 2012. Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet no. 311 [report online]. Available from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html Accessed 12 November 2012
-
- Wing RR, Hill JO. Successful weight loss maintenance. Annu Rev Nutr 2001;21:323–341 - PubMed
-
- Smoliga JM, Baur JA, Hausenblas HA. Resveratrol and health—a comprehensive review of human clinical trials. Mol Nutr Food Res 2011;55:1129–1141 - PubMed
-
- Stervbo U, Vang O, Bonnesen C. A review of the content of the putative chemopreventive phytoalexin resveratrol in red wine. Food Chem 2007;101:449–457
Publication types
- Actions (V体育2025版)
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

