"VSports注册入口" MDM2 and MDMX: Alone and together in regulation of p53
- PMID: 23002429
- PMCID: PMC3448287
VSports注册入口 - MDM2 and MDMX: Alone and together in regulation of p53
Abstract
p53, a critical tumor suppressor, is activated by various cellular stresses to prevent and repair damages that can lead to tumor development. In response to these stresses, p53 activation can cause very serious cellular effects including permanent cell cycle arrest and cell death. p53 must therefore be very tightly regulated to avoid unnecessary pathological effects. The homologs MDM2 and MDMX have been shown to be the major, essential negative regulators of p53. In normal cells, MDM2 and MDMX suppress p53 activity, but in the event of cellular stress, they themselves must be inhibited so that p53 may respond to the stress VSports手机版. MDM2 and MDMX are known to bind together, and play multifaceted, non-redundant roles in modulating p53 protein activity. Recently, evidence has emerged showing that MDM2 and MDMX most effectively inhibit p53 as a complex, and possibly play non-redundant roles because they must function as one to control p53. In this review, we give an overview of MDM2 and MDMX and discuss a few ways in which they are modified so that p53 may be activated. Lastly, we discuss the non-redundant roles of MDM2 and MDMX and how it is important to investigate the effect on the complex as a whole when investigating either protein. .
V体育安卓版 - Conflict of interest statement
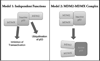
Figures (V体育ios版)
"V体育平台登录" References
-
- Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, et al. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991;253:49–53. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL, et al. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992;356:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Jacks T, Remington L, Williams BO, et al. Tumor spectrum analysis in p53-mutant mice. Curr Biol. 1994;4:1–7. - PubMed
-
- el-Deiry WS. Regulation of p53 downstream genes. Semin Cancer Biol. 1998;8:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Bode AM, Dong Z. Post-translational modification of p53 in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:793–805. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (VSports)
Miscellaneous (VSports最新版本)
