Phospho-ΔNp63α/SREBF1 protein interactions: bridging cell metabolism and cisplatin chemoresistance
- PMID: 22951905
- PMCID: PMC3495824
- DOI: "VSports" 10.4161/cc.22022
Phospho-ΔNp63α/SREBF1 protein interactions: bridging cell metabolism and cisplatin chemoresistance (VSports)
Abstract
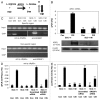
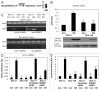
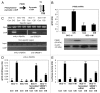
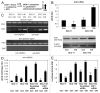
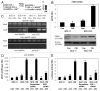
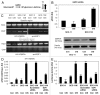
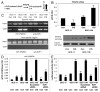
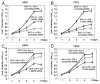
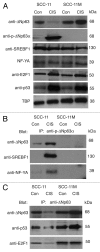
Tumor protein (TP)-p53 family members (TP63, TP63 and TP73) are guardians of the genome and key players in orchestrating the cellular response to cisplatin treatment VSports手机版. Cisplatin-induced phosphorylation of ΔNp63α was shown to have a role in regulating intracellular ΔNp63α protein levels. We previously found that squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells exposed to cisplatin displayed the ATM-dependent phosphorylation of ΔNp63α (p-ΔNp63α), which is critical for the transcriptional regulation of specific downstream mRNAs and microRNAs and is likely to underlie the chemoresistance of SCC cells. However, SCC cells expressing non-p-ΔNp63α became more cisplatin-resistant. We also found that p-ΔNp63α forms complexes with a number of proteins involved in cell death response through regulation of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, autophagy, RNA splicing and chromatin modifications. Here, we showed that p-ΔNp63α induced ARG1, GAPDH, and CPT2 gene transcription in cisplatin-sensitive SCC cells, while non-p-ΔNp63α increased a transcription of CAD, G6PD and FASN genes in cisplatin-resistant SCC cells. We report that the p-ΔNp63α-dependent regulatory mechanisms implicated in the modulation of plethora of pathways, including amino acid, carbohydrate, lipid and nucleotide metabolisms, thereby affect tumor cell response to cisplatin-induced cell death, suggesting that the ATM-dependent ΔNp63α pathway plays a role in the resistance of tumor cells to platinum therapy. .
V体育官网 - Figures

References
-
- Zangen R, Ratovitski EA, Sidransky D. DeltaNp63α levels correlate with clinical tumor response to cisplatin. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1313–5. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.10.2066. - "VSports app下载" DOI - PubMed
-
- Kelland L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:573–84. doi: 10.1038/nrc2167. - V体育2025版 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels J, Martins I, Kepp O, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 2012;31:1869–83. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.384. - V体育官网入口 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical (V体育ios版)
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
