The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities (V体育官网入口)
- PMID: 22667998
- PMCID: "VSports app下载" PMC3545354
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2011.4391
The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
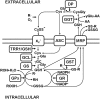
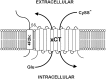
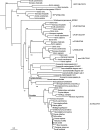
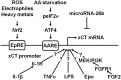
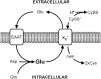
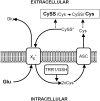
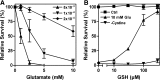
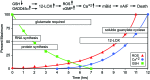
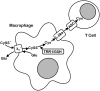
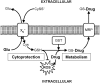
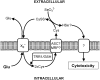
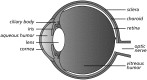
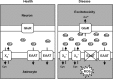
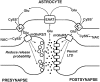
The antiporter system x(c)(-) imports the amino acid cystine, the oxidized form of cysteine, into cells with a 1:1 counter-transport of glutamate. It is composed of a light chain, xCT, and a heavy chain, 4F2 heavy chain (4F2hc), and, thus, belongs to the family of heterodimeric amino acid transporters. Cysteine is the rate-limiting substrate for the important antioxidant glutathione (GSH) and, along with cystine, it also forms a key redox couple on its own. Glutamate is a major neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS). By phylogenetic analysis, we show that system x(c)(-) is a rather evolutionarily new amino acid transport system. In addition, we summarize the current knowledge regarding the molecular mechanisms that regulate system x(c)(-), including the transcriptional regulation of the xCT light chain, posttranscriptional mechanisms, and pharmacological inhibitors of system x(c)(-). Moreover, the roles of system x(c)(-) in regulating GSH levels, the redox state of the extracellular cystine/cysteine redox couple, and extracellular glutamate levels are discussed. In vitro, glutamate-mediated system x(c)(-) inhibition leads to neuronal cell death, a paradigm called oxidative glutamate toxicity, which has successfully been used to identify neuroprotective compounds VSports手机版. In vivo, xCT has a rather restricted expression pattern with the highest levels in the CNS and parts of the immune system. System x(c)(-) is also present in the eye. Moreover, an elevated expression of xCT has been reported in cancer. We highlight the diverse roles of system x(c)(-) in the regulation of the immune response, in various aspects of cancer and in the eye and the CNS. .
"VSports手机版" Figures
References
-
- Aharoni-Simon M. Reifen R. Tirosh O. ROS-production-mediated activation of AP-1 but not NFkappaB inhibits glutamate-induced HT4 neuronal cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:1339–1349. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht P. Lewerenz J. Dittmer S. Noack R. Maher P. Methner A. Mechanisms of oxidative glutamate toxicity: the glutamate/cystine antiporter system xc− as a neuroprotective drug target. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010;9:373–382. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CL. Iyer SS. Ziegler TR. Jones DP. Control of extracellular cysteine/cystine redox state by HT-29 cells is independent of cellular glutathione. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;293:R1069–R1075. - PubMed
-
- Antonini B. Piva S. Paltenghi M. Candiani A. Latronico N. The early phase of critical illness is a progressive acidic state due to unmeasured anions. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008;25:566–571. - PubMed
-
- Asanuma M. Miyazaki I. Diaz-Corrales FJ. Kimoto N. Kikkawa Y. Takeshima M. Miyoshi K. Murata M. Neuroprotective effects of zonisamide target astrocyte. Ann Neurol. 2010;67:239–249. - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育ios版)
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

