Metronomic dosing of BH3 mimetic small molecule yields robust antiangiogenic and antitumor effects
- PMID: 22158856
- PMCID: "V体育安卓版" PMC3748951
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2873
Metronomic dosing of BH3 mimetic small molecule yields robust antiangiogenic and antitumor effects
Abstract (V体育官网入口)
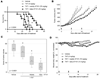
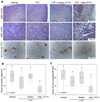
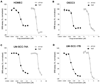
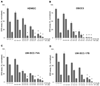
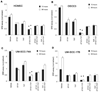
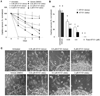
Bcl-2 is an antiapoptotic protein that has also been found to function as a proangiogenic signaling molecule. Improvements in antiangiogenic therapy can be engendered by metronomic dosing. Thus, we hypothesized that BH3-mimetic drugs that antagonize Bcl-2 family proteins may exert a greater efficacy when dosed metronomically. To examine this hypothesis, we employed AT101, an orally available and well-tolerated BH3-mimetic drug that has been established as effective. In a mouse xenograft model of human squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) that includes a humanized vasculature, we explored the effects of docetaxel in combination with either daily (metronomic) or weekly (bolus) doses of AT101. In addition, we explored the effect of single or combination therapy on angiogenesis and survival of endothelial or SCC cells in vitro VSports手机版. Metronomic AT101 therapy increased mouse survival, decreased tumor mitotic index, and decreased tumor microvessel density, compared with bolus therapy. Therapeutic potentiation was achieved by similar overall drug exposure and without altering systemic toxicities. Combinations of AT101 and docetaxel produced additive toxicity in both endothelial and SCC tumor cells. Notably, subapoptotic concentrations of AT101 potently inhibited the angiogenic potential of endothelial cells. Taken together, our findings unveil the efficacious benefits that can be achieved by metronomic delivery of BH3-mimetic drugs, in particular suggesting that SCC patients with might benefit from low-dose continuous administration of these drugs. .
©2011 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement (VSports app下载)
"V体育ios版" Figures
References
-
- Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR, Mickiewicz E, Winquist E, Gorbounova V, et al. Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1705–1715. - VSports app下载 - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C, Gorlia T, Mesia R, Degardin M, et al. Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1695–1704. - PubMed
-
- Langer CJ. Targeted therapy in head and neck cancer: State of the art 2007 and review of clinical applications. Cancer. 2008;112:2635–2645. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
"V体育平台登录" Grants and funding
- "V体育2025版" P50 CA097248/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19-CA113317/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DE15948/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA97248/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (VSports注册入口)
- R01 DE014601/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States (VSports最新版本)
- R01 DE021139/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DE14601/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016586/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DE16586/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE015948/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R21-DE19279/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports注册入口" U19 CA113317/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育官网" R21 DE019279/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
"V体育安卓版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

