"V体育平台登录" Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway: role in tumor progression and therapeutic implications in breast cancer
- PMID: 22114931
- PMCID: PMC3315683
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3039
Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway: role in tumor progression and therapeutic implications in breast cancer
Abstract
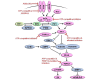
Mutations in genes that constitute the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway occur in >70% of breast cancers. Clinical and experimental evidence suggest that PI3K pathway activation promotes resistance to some of the current breast cancer therapies. PI3K is a major signaling hub downstream of human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)2 and other receptor tyrosine kinases. PI3K activates AKT, serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase (SGK), phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and several other molecules involved in cell cycle progression and survival. In estrogen receptor (ER)+ breast cancer cells, PI3K activation promotes estrogen-dependent and -independent ER transcriptional activity, which, in turn, may contribute to anti-estrogen resistance. Activation of this pathway also confers resistance to HER2-targeted therapies. In experimental models of resistance to anti-estrogens and HER2 inhibitors, pharmacological inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR has been shown to overcome drug resistance. Early clinical data suggest that combined inhibition of either HER2 or ER plus inhibition of the PI3K pathway might be an effective strategy for treatment of respective HER2+ and ER+ breast cancers resistant to standard therapies VSports手机版. Here, we review alterations in the PI3K pathway in breast cancer, their association with therapeutic resistance, and the state of clinical development of PI3K pathway inhibitors. .
Figures

References
-
- Guertin DA, Sabatini DM. Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Isakoff SJ, Engelman JA, Irie HY, Luo J, Brachmann SM, Pearline RV, Cantley LC, Brugge JS. Breast cancer-associated PIK3CA mutations are oncogenic in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10992–11000. - PubMed
-
- Meyer DS, Brinkhaus H, Muller U, Muller M, Cardiff RD, Bentires-Alj M. Luminal expression of PIK3CA mutant H1047R in the mammary gland induces heterogeneous tumors. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4344–4351. - PubMed
-
- Liu P, Cheng H, Santiago S, Raeder M, Zhang F, Isabella A, Yang J, Semaan DJ, Chen C, Fox EA, Gray NS, Monahan J, Schlegel R, Beroukhim R, Mills GB, Zhao JJ. Oncogenic PIK3CA-driven mammary tumors frequently recur via PI3K pathway-dependent and PI3K pathway-independent mechanisms. Nat Med. 2011;17:1116–1120. - "VSports手机版" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
"V体育官网" Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

