"V体育官网" Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent carboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth and viability
- PMID: 22106302
- PMCID: PMC3241793
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1117773108
Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent carboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth and viability
V体育安卓版 - Abstract
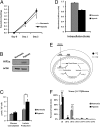
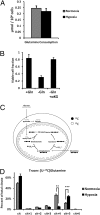
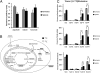
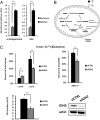
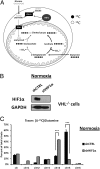
Citrate is a critical metabolite required to support both mitochondrial bioenergetics and cytosolic macromolecular synthesis. When cells proliferate under normoxic conditions, glucose provides the acetyl-CoA that condenses with oxaloacetate to support citrate production. Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle anaplerosis is maintained primarily by glutamine. Here we report that some hypoxic cells are able to maintain cell proliferation despite a profound reduction in glucose-dependent citrate production. In these hypoxic cells, glutamine becomes a major source of citrate. Glutamine-derived α-ketoglutarate is reductively carboxylated by the NADPH-linked mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH2) to form isocitrate, which can then be isomerized to citrate. The increased IDH2-dependent carboxylation of glutamine-derived α-ketoglutarate in hypoxia is associated with a concomitant increased synthesis of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG) in cells with wild-type IDH1 and IDH2. When either starved of glutamine or rendered IDH2-deficient by RNAi, hypoxic cells are unable to proliferate. The reductive carboxylation of glutamine is part of the metabolic reprogramming associated with hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1), as constitutive activation of HIF1 recapitulates the preferential reductive metabolism of glutamine-derived α-ketoglutarate even in normoxic conditions. These data support a role for glutamine carboxylation in maintaining citrate synthesis and cell growth under hypoxic conditions VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
"V体育ios版" References
-
- Hatzivassiliou G, et al. ATP citrate lyase inhibition can suppress tumor cell growth. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:311–321. - PubMed
VSports在线直播 - Publication types
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Grants and funding
V体育官网 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports在线直播 - Other Literature Sources
"VSports手机版" Miscellaneous

