The metabolome of induced pluripotent stem cells reveals metabolic changes occurring in somatic cell reprogramming
- PMID: 22064701
- PMCID: "VSports app下载" PMC3252494
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2011.177
"VSports注册入口" The metabolome of induced pluripotent stem cells reveals metabolic changes occurring in somatic cell reprogramming
Abstract
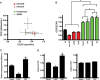
Metabolism is vital to every aspect of cell function, yet the metabolome of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) remains largely unexplored. Here we report, using an untargeted metabolomics approach, that human iPSCs share a pluripotent metabolomic signature with embryonic stem cells (ESCs) that is distinct from their parental cells, and that is characterized by changes in metabolites involved in cellular respiration. Examination of cellular bioenergetics corroborated with our metabolomic analysis, and demonstrated that somatic cells convert from an oxidative state to a glycolytic state in pluripotency. Interestingly, the bioenergetics of various somatic cells correlated with their reprogramming efficiencies VSports手机版. We further identified metabolites that differ between iPSCs and ESCs, which revealed novel metabolic pathways that play a critical role in regulating somatic cell reprogramming. Our findings are the first to globally analyze the metabolome of iPSCs, and provide mechanistic insight into a new layer of regulation involved in inducing pluripotency, and in evaluating iPSC and ESC equivalence. .
Figures (VSports最新版本)
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
-
- Panopoulos AD, Ruiz S, Izpisua Belmonte JC. iPSCs: induced back to controversy. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8:347–348. - PubMed
V体育官网 - Publication types
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育官网" Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

