Solute carrier protein family may involve in radiation-induced radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 21909646
- PMCID: VSports手机版 - PMC11828279
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-011-1050-9
V体育2025版 - Solute carrier protein family may involve in radiation-induced radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To find new signaling pathways that may be involved in the cellular response to ionizing radiation VSports手机版. .
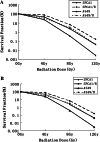
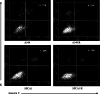
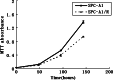
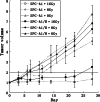
Methods: Two radioresistant subclones (A549/R and SPCA1/R) derived from lung adenocarcinoma cell lines A549 and SPCA1 were established after eight rounds of sublethal irradiation. The new subclones were tested for radioresistant features using clonogenic assay and apoptosis analysis. The genes expressed differentially were screened with cDNA microarray analysis consisting of 48,000 transcript probes and confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR V体育安卓版. .
Results: Stable and significant radioresistance was observed in the screened subclones V体育ios版. The microarray analysis showed 65 genes were up-regulated and 141 genes down-regulated in SPCA1/R cells. The up-regulated and down-regulated genes were 708 and 230 in A549/R cells, respectively. Twenty-seven altered genes were consistent in both subclones. Interestingly, members the of human solute carrier (SLC) gene superfamily were among in 27 genes. .
Conclusions: The differentially expressed genes in both cell lines may contribute to their radioresistant phenotype VSports最新版本. This extensive list of genes identified in the experiment provides a large body of potentially valuable information for studying the molecular mechanism(s) of radiosensitivity and identification of candidate molecular markers of radiation sensitivity. Thus, to our knowledge, the SLC gene superfamily is the first being reported to involve in acquired radioresistance. .
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chaudhry MA (2006) Radiation-induced gene expression profile of human cells deficient in 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanine glycosylase. Int J Cancer 118(3):633–642. doi:10.1002/ijc.21392 - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- de Vries B, Mamsa H, Stam AH, Wan J, Bakker SL, Vanmolkot KR, Haan J, Terwindt GM, Boon EM, Howard BD, Frants RR, Baloh RW, Ferrari MD, Jen JC, van den Maagdenberg AM (2009) Episodic ataxia associated with EAAT1 mutation C186S affecting glutamate reuptake. Arch Neurol 66(1):97–101. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2008.535 - "VSports" PubMed
-
- Dornan D, Shimizu H, Mah A, Dudhela T, Eby M, O’Rourke K, Seshagiri S, Dixit VM (2006) ATM engages autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 after DNA damage. Science 313(5790):1122–1126. doi:10.1126/science.1127335 - PubMed
-
- Dritschilo A, Huang CH, Rudin CM, Marshall J, Collins B, Dul JL, Zhang C, Kumar D, Gokhale PC, Ahmad A, Ahmad I, Sherman JW, Kasid UN (2006) Phase I study of liposome-encapsulated c-raf antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide infusion in combination with radiation therapy in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 12(4):1251–1259. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1260 - PubMed
-
- Fukuda K, Sakakura C, Miyagawa K, Kuriu Y, Kin S, Nakase Y, Hagiwara A, Mitsufuji S, Okazaki Y, Hayashizaki Y, Yamagishi H (2004) Differential gene expression profiles of radioresistant oesophageal cancer cell lines established by continuous fractionated irradiation. Br J Cancer 91(8):1543–1550. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602187 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports手机版 - Actions
MeSH terms (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
VSports - Full Text Sources
Medical

