"V体育官网" Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1 (ALDH7A1) attenuates reactive aldehyde and oxidative stress induced cytotoxicity
- PMID: 21338592
- PMCID: PMC3387551
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2011.02.016 (V体育安卓版)
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1 (ALDH7A1) attenuates reactive aldehyde and oxidative stress induced cytotoxicity
Abstract
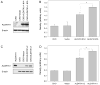
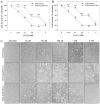
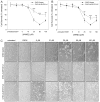
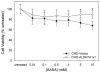
Mammalian aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1 (ALDH7A1) is homologous to plant ALDH7B1 which protects against various forms of stress such as increased salinity, dehydration and treatment with oxidants or pesticides VSports手机版. Deleterious mutations in human ALDH7A1 are responsible for pyridoxine-dependent and folinic acid-responsive seizures. In previous studies, we have shown that human ALDH7A1 protects against hyperosmotic stress presumably through the generation of betaine, an important cellular osmolyte, formed from betaine aldehyde. Hyperosmotic stress is coupled to an increase in oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation (LPO). In this study, cell viability assays revealed that stable expression of mitochondrial ALDH7A1 in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells provides significant protection against treatment with the LPO-derived aldehydes hexanal and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4HNE) implicating a protective function for the enzyme during oxidative stress. A significant increase in cell survival was also observed in CHO cells expressing either mitochondrial or cytosolic ALDH7A1 treated with increasing concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) or 4HNE, providing further evidence for anti-oxidant activity. In vitro enzyme activity assays indicate that human ALDH7A1 is sensitive to oxidation and that efficiency can be at least partially restored by incubating recombinant protein with the thiol reducing agent β-mercaptoethanol (BME). We also show that after reactivation with BME, recombinant ALDH7A1 is capable of metabolizing the reactive aldehyde 4HNE. In conclusion, ALDH7A1 mechanistically appears to provide cells protection through multiple pathways including the removal of toxic LPO-derived aldehydes in addition to osmolyte generation. .
Copyright © 2011 V体育安卓版. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Guerrero FD, Jones JT, Mullet JE. Turgor-responsive gene transcription and RNA levels increase rapidly when pea shoots are wilted. Sequence and expression of three inducible genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1990;15:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Stroeher VL, Boothe JG, Good AG. Molecular cloning and expression of a turgor-responsive gene in Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol. 1995;27:541–551. - PubMed
-
- Valente MA, Faria JA, Soares-Ramos JR, Reis PA, Pinheiro GL, Piovesan ND, Morais AT, Menezes CC, Cano MA, Fietto LG, Loureiro ME, Aragao FJ, Fontes EP. The ER luminal binding protein (BiP) mediates an increase in drought tolerance in soybean and delays drought-induced leaf senescence in soybean and tobacco. J Exp Bot. 2009;60:533–546. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues SM, Andrade MO, Gomes AP, Damatta FM, Baracat-Pereira MC, Fontes EP. Arabidopsis and tobacco plants ectopically expressing the soybean antiquitin-like ALDH7 gene display enhanced tolerance to drought, salinity, and oxidative stress. J Exp Bot. 2006;57:1909–1918. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Mills PB, Struys E, Jakobs C, Plecko B, Baxter P, Baumgartner M, Willemsen MA, Omran H, Tacke U, Uhlenberg B, Weschke B, Clayton PT. Mutations in antiquitin in individuals with pyridoxine-dependent seizures. Nat Med. 2006;12:307–309. - PubMed (V体育安卓版)
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous (V体育官网入口)

