Remote postconditioning by humoral factors in effluent from ischemic preconditioned rat hearts is mediated via PI3K/Akt-dependent cell-survival signaling at reperfusion
- PMID: 21103992
- PMCID: "V体育安卓版" PMC3012213
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-010-0133-0
Remote postconditioning by humoral factors in effluent from ischemic preconditioned rat hearts is mediated via PI3K/Akt-dependent cell-survival signaling at reperfusion (V体育安卓版)
Abstract
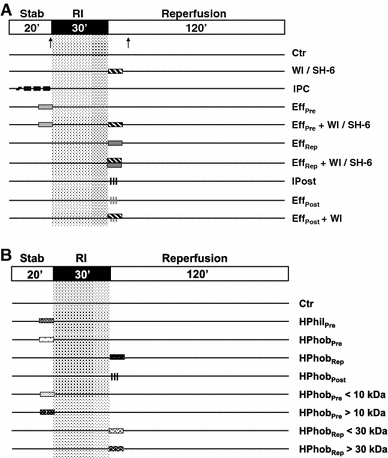
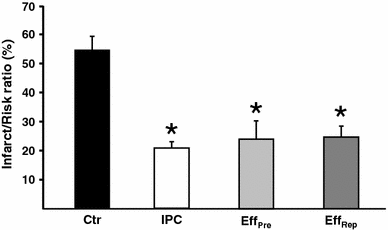
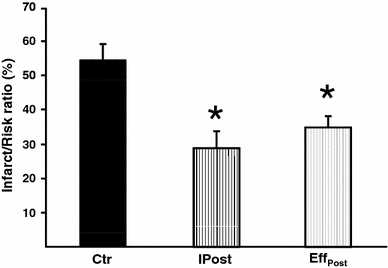
Short non-lethal ischemic episodes administered to hearts prior to (ischemic preconditioning, IPC) or directly after (ischemic postconditioning, IPost) ischemic events facilitate myocardial protection. Transferring coronary effluent collected during IPC treatment to un-preconditioned recipient hearts protects from lethal ischemic insults. We propose that coronary IPC effluent contains hydrophobic cytoprotective mediators acting via PI3K/Akt-dependent pro-survival signaling at ischemic reperfusion. Ex vivo rat hearts were subjected to 30 min of regional ischemia and 120 min of reperfusion. IPC effluent administered for 10 min prior to index ischemia attenuated infarct size by ≥55% versus control hearts (P < 0. 05). Effluent administration for 10 min at immediate reperfusion (reperfusion therapy) or as a mimetic of pharmacological postconditioning (remote postconditioning, RIPost) significantly reduced infarct size compared to control (P < 0. 05) VSports手机版. The IPC effluent significantly increased Akt phosphorylation in un-preconditioned hearts when administered before ischemia or at reperfusion, while pharmacological inhibition of PI3K/Akt-signaling at reperfusion completely abrogated the cardioprotection offered by effluent administration. Fractionation of coronary IPC effluent revealed that cytoprotective humoral mediator(s) released during the conditioning phase were of hydrophobic nature as all hydrophobic fractions with molecules under 30 kDa significantly reduced infarct size versus the control and hydrophilic fraction-treated hearts (P < 0. 05). The total hydrophobic effluent fraction significantly reduced infarct size independently of temporal administration (before ischemia, at reperfusion or as remote postconditioning). In conclusion, the IPC effluent retains strong cardioprotective properties, containing hydrophobic mediator(s) < 30 kDa offering cytoprotection via PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling at ischemic reperfusion. .
VSports app下载 - Figures

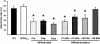
References
-
- Anderson KE, Coadwell J, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT. Translocation of PDK-1 to the plasma membrane is important in allowing PDK-1 to activate protein kinase B. Curr Biol. 1998;8(12):684–691. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(98)70274-X. - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cohen MV, Downey JM. Adenosine: trigger and mediator of cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103(3):203–215. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0687-7. - "V体育安卓版" DOI - PubMed
-
- Davidson SM, Hausenloy D, Duchen, Yellon DM. Signalling via the reperfusion injury signalling kinase (risk) pathway links closure of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to cardioprotection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(3):414–419. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.09.017. - V体育2025版 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dickson EW, Lorbar M, Porcaro WA, Fenton RA, Reinhardt CP, Gysembergh A, Przyklenk K. Rabbit heart can be “preconditioned” via transfer of coronary effluent. Am J Physiol. 1999;277(6 Pt 2):H2451–H2457. - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

