V体育ios版 - Evaluation of FTIR spectroscopy as a diagnostic tool for lung cancer using sputum
- PMID: 21092279
- PMCID: PMC3000851
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-640
Evaluation of FTIR spectroscopy as a diagnostic tool for lung cancer using sputum (VSports最新版本)
Abstract
Background: Survival time for lung cancer is poor with over 90% of patients dying within five years of diagnosis primarily due to detection at late stage. The main objective of this study was to evaluate Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) as a high throughput and cost effective method for identifying biochemical changes in sputum as biomarkers for detection of lung cancer VSports手机版. .
Methods: Sputum was collected from 25 lung cancer patients in the Medlung observational study and 25 healthy controls V体育安卓版. FTIR spectra were generated from sputum cell pellets using infrared wavenumbers within the 1800 to 950 cm-1 "fingerprint" region. .
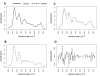
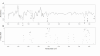
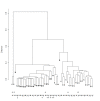
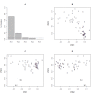
Results: A panel of 92 infrared wavenumbers had absorbances significantly different between cancer and normal sputum spectra and were associated with putative changes in protein, nucleic acid and glycogen levels in tumours. Five prominent significant wavenumbers at 964 cm-1, 1024 cm-1, 1411 cm-1, 1577 cm-1 and 1656 cm-1 separated cancer spectra from normal spectra into two distinct groups using multivariate analysis (group 1: 100% cancer cases; group 2: 92% normal cases). Principal components analysis revealed that these wavenumbers were also able to distinguish lung cancer patients who had previously been diagnosed with breast cancer. No patterns of spectra groupings were associated with inflammation or other diseases of the airways. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that FTIR applied to sputum might have high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing lung cancer with potential as a non-invasive, cost-effective and high-throughput method for screening. VSports最新版本.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials. gov: NCT00899262. V体育平台登录.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer, Fact Sheets, World Health Organization. 2009. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/
-
- Cancer Stats, Mortality-UK Cancer Research UK. 2006. http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/types/lung/
-
- Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, Thun M, Heath C, Jr, Doll R. Mortality from smoking in developed countries 1950-2000: Indirect estimates from National Vital Statistics. Oxford University Press; 2006.
-
- Field JK, Duffy SW. Lung cancer screening: the way forward. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:557–62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604509. - VSports手机版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms (VSports手机版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
VSports手机版 - Associated data
- Actions (VSports)
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
"V体育ios版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

