VSports注册入口 - FcγRIV deletion reveals its central role for IgG2a and IgG2b activity in vivo
- PMID: 20974962
- PMCID: PMC2984189
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1014515107 (VSports在线直播)
FcγRIV deletion reveals its central role for IgG2a and IgG2b activity in vivo
VSports在线直播 - Abstract
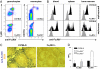
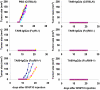
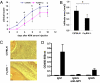
Cellular Fcγ receptors are essential for IgG-dependent effector functions in vivo. There is convincing evidence that selective activating Fcγ receptors are responsible for the activity of individual IgG subclasses. Thus, IgG1 activity is absent in FcγRIII-deficient mice, and several studies suggest that the activity of the most potent IgG subclasses, IgG2a and IgG2b, might be dependent on either individual or a combination of activating FcγRs. To study the role of individual activating FcγRs for IgG subclass activity, we generated an FcγRIV-deficient mouse and showed that a variety of IgG2a- and IgG2b-dependent effector functions are impaired in the absence of this activating Fc receptor in models of autoimmunity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
"VSports app下载" Figures
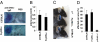
References
-
- Hogarth PM. Fc receptors are major mediators of antibody based inflammation in autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:798–802. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Antibody-mediated modulation of immune responses. Immunol Rev. 2010;236:265–275. - PubMed
-
- Takai T. Roles of Fc receptors in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:580–592. - PubMed
-
- Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:34–47. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch JV, Clynes RA. Divergent roles for Fc receptors and complement in vivo. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:421–432. - PubMed
Publication types
VSports手机版 - MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
"VSports手机版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

