"V体育安卓版" Pancreatic cancers epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress miR-200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR-200a and miR-200b levels
- PMID: 20551052
- PMCID: PMC3130565
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4227
V体育官网入口 - Pancreatic cancers epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress miR-200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR-200a and miR-200b levels
Abstract
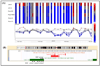
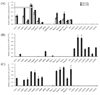
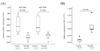
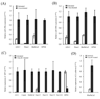
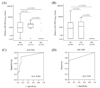
Aberrant DNA methylation and microRNA expression play important roles in the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. While interrogating differentially methylated CpG islands in pancreatic cancer, we identified two members of miR-200 family, miR-200a and miR-200b, that were hypomethylated and overexpressed in pancreatic cancer. We also identified prevalent hypermethylation and silencing of one of their downstream targets, SIP1 (ZFHX1B, ZEB2), whose protein product suppresses E-cadherin expression and contributes to epithelial mesenchymal transition. In a panel of 23 pancreatic cell lines, we observed a reciprocal correlation between miR-200, SIP1, and E-cadherin expression, with pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts showing the opposite expression pattern to most pancreatic cancers. In Panc-1 cells, which express SIP1, have low E-cadherin expression, and do not express miR-200a or miR-200b, treatment with miR-200a and miR-200b downregulated SIP1 mRNA and increased E-cadherin expression. However, most pancreatic cancers express miR-200a and miR-200b, but this expression does not affect SIP1 expression, as the SIP1 promoter is silenced by hypermethylation and in these cancers E-cadherin is generally expressed. Both miR-200a and miR-200b were significantly elevated in the sera of pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis patients compared with healthy controls (P < 0. 0001), yielding receiver operating characteristic curve areas of 0. 861 and 0. 85, respectively VSports手机版. In conclusion, most pancreatic cancers display hypomethylation and overexpression of miR-200a and miR-200b, silencing of SIP1 by promoter methylation, and retention of E-cadherin expression. The elevated serum levels of miR-200a and miR-200b in most patients with pancreatic cancer could have diagnostic utility. .
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Hruban R, Klein A, Eshleman J, Axilbund J, Goggins M. Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Expert Review in Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2007;1:81–88. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Canto MI, Goggins M, Hruban RH, et al. Screening for early pancreatic neoplasia in high-risk individuals: a prospective controlled study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:766–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
"V体育ios版" Substances
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育平台登录)
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

