VSports最新版本 - New insights into checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network
- PMID: 20068082
- PMCID: PMC2939735
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1029
VSports - New insights into checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network
Abstract
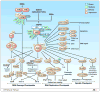
The DNA damage response (DDR) represents a complex network of multiple signaling pathways involving cell cycle checkpoints, DNA repair, transcriptional programs, and apoptosis, through which cells maintain genomic integrity following various endogenous (metabolic) or environmental stresses. In cancer treatment, the DDR occurs in response to various genotoxic insults by diverse cytotoxic agents and radiation, representing an important mechanism limiting chemotherapeutic and radiotherapeutic efficacy. This has prompted the development of agents targeting DDR signaling pathways, particularly checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1), which contributes to all currently defined cell cycle checkpoints, including G1/S, intra-S-phase, G2/M, and the mitotic spindle checkpoint. Although numerous agents have been developed with the primary goal of enhancing the activity of DNA-damaging agents or radiation, the therapeutic outcome of this strategy remains to be determined. Recently, new insights into DDR signaling pathways support the notion that Chk1 represents a core component central to the entire DDR, including direct involvement in DNA repair and apoptotic events in addition to checkpoint regulation. Together, these new insights into the role of Chk1 in the DDR machinery could provide an opportunity for novel approaches to the development of Chk1 inhibitor strategies VSports手机版. .
Figures (VSports app下载)
References
-
- Bartek J, Lukas J. DNA damage checkpoints: from initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:238–245. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Zhou BB, Anderson HJ, Roberge M. Targeting DNA checkpoint kinases in cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2(4 Suppl 1):S16–S22. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
-
- Branzei D, Foiani M. Regulation of DNA repair throughout the cell cycle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:297–308. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
-
- Lobrich M, Jeggo PA. The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Kastan MB, Bartek J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:316–323. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
VSports app下载 - Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
V体育官网入口 - Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

