"V体育官网入口" Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate phosphorylation promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis via the protein kinase C-dependent pathway
- PMID: 20047593
- PMCID: PMC11158558
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01427.x
Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate phosphorylation promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis via the protein kinase C-dependent pathway
Abstract
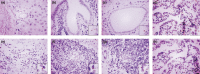
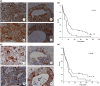
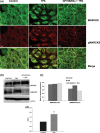
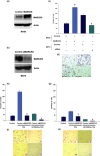
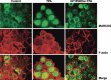
Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS), a substrate of protein kinase C (PKC) has been suggested to be implicated in cell adhesion, secretion, and motility through the regulation of the actin cytoskeletal structure. The quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed that MARCKS is significantly overexpressed in Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) (P = 0. 001) in a hamster model, which correlated with the results of mRNA in situ hybridization. An immunohistochemical analysis of 60 CCA patients revealed a significant increase of MARCKS expression. Moreover, the log-rank analysis indicated that CCA patients with a high MARCKS expression have significantly shorter survival times than those with a low MARCKS expression (P = 0. 02). This study investigated whether MARCKS overexpression is associated with CCA metastasis. Using a confocal microscopic analysis of CCA cell lines that had been stimulated with the PKC activator, 12-0-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate (TPA), MARCKS was found to be translocated from the plasma membrane to the perinuclear area. In addition, phosphorylated MARCKS (pMARCKS) became highly concentrated in the perinuclear area VSports手机版. Moreover, an adhesion assay demonstrated that the exogenous overexpression of MARCKS remarkably promoted cell attachment. Interestingly, after TPA stimulation, the CCA cell line-depleted MARCKS showed a decrease in migration and invasion activity. It can be concluded that in non-stimulation, MARCKS promotes cell attachment to the extracellular matrix. After TPA stimulation, PKC phosphorylates MARCKS leading to cell migration or invasion. Taken together, the results of this study reveal a prominent role for MARCKS as one of the key players in the migration of CCA cells and suggest that cycling between MARCKS and pMARCKS can regulate the metastasis of biliary cancer cells. .
Figures (V体育安卓版)

References
-
- Elkins DB, Haswell‐Elkins MR, Mairiang E et al. A high frequency of hepatobiliary disease and suspected cholangiocarcinoma associated with heavy Opisthorchis viverrini infection in a small community in north‐east Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1990; 84 (5): 715–9. - PubMed
-
- Elkins DB, Mairiang E, Sithithaworn P et al. Cross‐sectional patterns of hepatobiliary abnormalities and possible precursor conditions of cholangiocarcinoma associated with Opisthorchis viverrini infection in humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1996; 55 (3): 295–301. - PubMed
-
- Haswell‐Elkins MR, Mairiang E, Mairiang P et al. Cross‐sectional study of Opisthorchis viverrini infection and cholangiocarcinoma in communities within a high‐risk area in northeast Thailand. Int J Cancer 1994; 59 (4): 505–9. - VSports - PubMed
-
- Flavell DJ, Lucas SB. Promotion of N‐nitrosodimethylamine‐initiated bile duct carcinogenesis in the hamster by the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini . Carcinogenesis 1983; 4 (7): 927–30. - PubMed
-
- Ohshima H, Bartsch H. Chronic infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors: possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 1994; 305 (2): 253–64. - PubMed
"VSports" Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
"V体育官网入口" MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
"VSports最新版本" Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
"V体育2025版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports手机版" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

