Regulation of membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase by SLUG contributes to hypoxia-mediated metastasis (VSports手机版)
- PMID: 20019845
- PMCID: PMC2794518
- DOI: "VSports在线直播" 10.1593/neo.91326
Regulation of membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase by SLUG contributes to hypoxia-mediated metastasis
Abstract
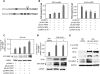
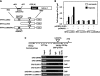
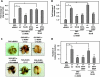
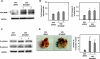
The hypoxic tumor environment has been shown to be critical to cancer metastasis through the promotion of angiogenesis, induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and acquisition of invasive potential VSports手机版. However, the impact of hypoxia on the expression profile of the proteolytic enzymes involved in invasiveness is relatively unknown. Membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP) is a glycosyl-phosphatidyl inositol-anchored protease that has been shown to be overexpressed in human cancers. However, detailed mechanisms regarding the regulation and function of MT4-MMP expression in tumor cells remain unknown. Here, we demonstrate that hypoxia or overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) induced MT4-MMP expression in human cancer cells. Activation of SLUG, a transcriptional factor regulating the EMT process of human cancers, by HIF-1alpha was critical for the induction of MT4-MMP under hypoxia. SLUG regulated the transcription of MT4-MMP through direct binding to the E-box located in its proximal promoter. Short-interference RNA-mediated knockdown of MT4-MMP attenuated in vitro invasiveness and in vivo pulmonary colonization of tumor cells without affecting cell migratory ability. MT4-MMP promoted invasiveness and pulmonary colonization through modulation of the expression profile of MMPs and angiogenic factors. Finally, coexpression of HIF-1alpha and MT4-MMP in human head and neck cancer was predictive of a worse clinical outcome. These findings establish a novel signaling pathway for hypoxia-mediated metastasis and elucidate the underlying regulatory mechanism and functional significance of MT4-MMP in cancer metastasis. .
Figures


References
-
- Harris AL. Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumor growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell PH. The HIF pathway in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005;16:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Yang MH, Wu KJ. TWIST activation by hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): implications in metastasis and development. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2090–2096. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
"VSports注册入口" Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网)
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources (VSports app下载)
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
