3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 potentiates upstream lesions on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in breast carcinoma
- PMID: 19602588
- PMCID: PMC2727605 (V体育安卓版)
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0820
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 potentiates upstream lesions on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in breast carcinoma (V体育2025版)
"V体育平台登录" Abstract
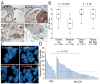
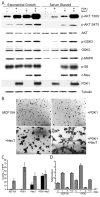
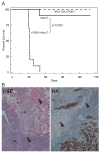
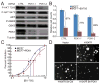
Lesions of ERBB2, PTEN, and PIK3CA activate the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway during cancer development by increasing levels of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP(3)). 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) is the first node of the PI3K signal output and is required for activation of AKT. PIP(3) recruits PDK1 and AKT to the cell membrane through interactions with their pleckstrin homology domains, allowing PDK1 to activate AKT by phosphorylating it at residue threonine-308. We show that total PDK1 protein and mRNA were overexpressed in a majority of human breast cancers and that 21% of tumors had five or more copies of the gene encoding PDK1, PDPK1. We found that increased PDPK1 copy number was associated with upstream pathway lesions (ERBB2 amplification, PTEN loss, or PIK3CA mutation), as well as patient survival. Examination of an independent set of breast cancers and tumor cell lines derived from multiple forms of human cancers also found increased PDK1 protein levels associated with such upstream pathway lesions. In human mammary cells, PDK1 enhanced the ability of upstream lesions to signal to AKT, stimulate cell growth and migration, and rendered cells more resistant to PDK1 and PI3K inhibition. After orthotopic transplantation, PDK1 overexpression was not oncogenic but dramatically enhanced the ability of ERBB2 to form tumors. Our studies argue that PDK1 overexpression and increased PDPK1 copy number are common occurrences in cancer that potentiate the oncogenic effect of upstream lesions on the PI3K pathway. Therefore, we conclude that alteration of PDK1 is a critical component of oncogenic PI3K signaling in breast cancer VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Isakoff SJ, Engelman JA, Irie HY, et al. Breast cancer-associated PIK3CA mutations are oncogenic in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10992–1000. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Li J, Simpson L, Takahashi M, et al. The PTEN/MMAC1 tumor suppressor induces cell death that is rescued by the AKT/protein kinase B oncogene. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5667–72. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, et al. Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell. 1998;95:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Zhou BP, Hu MC, Miller SA, et al. HER-2/neu blocks tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis via the Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:8027–31. - PubMed
"VSports最新版本" Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
"V体育平台登录" Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Grants and funding (V体育安卓版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Other Literature Sources
V体育平台登录 - Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

