VSports注册入口 - SMAD4 gene mutations are associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 19584151
- PMCID: PMC2819274
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0227
SMAD4 gene mutations are associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer (VSports最新版本)
Abstract
Purpose: Recently, the majority of protein coding genes were sequenced in a collection of pancreatic cancers, providing an unprecedented opportunity to identify genetic markers of prognosis for patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. VSports手机版.
Experimental design: We previously sequenced more than 750 million base pairs of DNA from 23,219 transcripts in a series of 24 adenocarcinomas of the pancreas V体育安卓版. In addition, 39 genes that were mutated in more than one of these 24 cancers were sequenced in a separate panel of 90 well-characterized adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. Of these 114 patients, 89 underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy, and the somatic mutations in these cancers were correlated with patient outcome. .
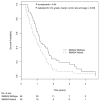
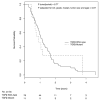
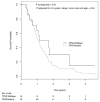
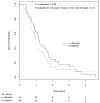
Results: When adjusted for age, lymph node status, margin status, and tumor size, SMAD4 gene inactivation was significantly associated with shorter overall survival (hazard ratio, 1. 92; 95% confidence interval, 1. 20-3. 05; P = 0. 006). Patients with SMAD4 gene inactivation survived a median of 11. 5 months, compared with 14 V体育ios版. 2 months for patients without SMAD4 inactivation. By contrast, mutations in CDKN2A or TP53 or the presence of multiple (> or =4) mutations or homozygous deletions among the 39 most frequently mutated genes were not associated with survival. .
Conclusions: SMAD4 gene inactivation is associated with poorer prognosis in patients with surgically resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. VSports最新版本.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:153–6. - PubMed
-
- Hruban RH, Pitman MB, Klimstra DS. Fourth Series, Fascicle. 6. Washington, DC: American Registry of Pathology and Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 2007. Tumors of the pancreas. Atlas of tumor pathology.
-
- Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, et al. Resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas - 616 patients: results, outcome, and prognostic indications. J Gastroenterol Surg. 2000;4:567–79. - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
V体育ios版 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

