"VSports注册入口" Genome-wide association study identifies five susceptibility loci for glioma
- PMID: 19578367
- PMCID: PMC4501476
- DOI: "VSports注册入口" 10.1038/ng.407
Genome-wide association study identifies five susceptibility loci for glioma
VSports手机版 - Abstract
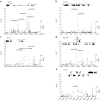
To identify risk variants for glioma, we conducted a meta-analysis of two genome-wide association studies by genotyping 550K tagging SNPs in a total of 1,878 cases and 3,670 controls, with validation in three additional independent series totaling 2,545 cases and 2,953 controls. We identified five risk loci for glioma at 5p15. 33 (rs2736100, TERT; P = 1. 50 x 10(-17)), 8q24. 21 (rs4295627, CCDC26; P = 2. 34 x 10(-18)), 9p21. 3 (rs4977756, CDKN2A-CDKN2B; P = 7. 24 x 10(-15)), 20q13. 33 (rs6010620, RTEL1; P = 2. 52 x 10(-12)) and 11q23. 3 (rs498872, PHLDB1; P = 1. 07 x 10(-8)). These data show that common low-penetrance susceptibility alleles contribute to the risk of developing glioma and provide insight into disease causation of this primary brain tumor VSports手机版. .
V体育官网入口 - Figures
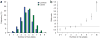
References
-
- Hemminki K, Li X. Familial risks in nervous system tumors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003;12:1137–1142. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Cardis E, et al. The INTERPHONE study: design, epidemiological methods, and description of the study population. Eur J Epidemiol. 2007;22:647–664. - PubMed
-
- Power C, Elliott J. Cohort profile: 1958 British birth cohort (National Child Development Study) Int J Epidemiol. 2006;35:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Hunter DJ, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2007;39:870–874. - VSports - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育安卓版)
Molecular Biology Databases
"V体育ios版" Miscellaneous

