Effect of T-705 treatment on western equine encephalitis in a mouse model
- PMID: 19428608
- PMCID: PMC2704019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.02.201
Effect of T-705 treatment on western equine encephalitis in a mouse model
Abstract
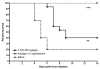
A mouse model of western equine encephalitis (WEE) was characterized for use in antiviral studies. Virus was detected in several tissues, most notably an average titer of 9. 5+/-1. 1 log(10) 50% cell culture infectious doses (CCID(50))/g tissue in the brains of infected animals. Signs of WEE included limb weakness, paralysis, involuntary spasms or extension of limbs, clenching of paws, hunching, ruffling of fur, and eye exudates, many of which are indicative of neurological disease. The pyrazinecarboxamide derivative, T-705, was found to be active in Vero cells against WEE virus (WEEV) with an 90% effective concentration (EC(90)) of 49microg/ml (selective index [SI]>20). Treatment with T-705 in this WEE mouse model resulted in significant improvement in survival and mean day to death after oral treatment administered twice a day for 7 days at a dose of 400mg/(kgd). Virus titer in the brain was not significantly reduced, despite a 1-log reduction in average brain titer in treated animals on 4dpi. Signs of disease were relatively mild in treated animals, but were not eliminated. Treatment with T-705 improved morbidity and mortality of WEEV-infected mice, further illustrating the broad-spectrum activity of T-705 in the treatment of RNA viruses VSports手机版. .
"VSports手机版" Figures


References
-
- Aguilar MJ. Pathological changes in brain and other target organs of infant and weanling mice after infection with non-neuroadapted western equine encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1970;2:533–542. - "V体育ios版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Toyama starts U.S. trials of polymerase inhibitor. RxTrials Institute Drug Pipeline Alert. 2007. http://www.fdanews.com/newsletter/article?articleId=91489&issueId=9890.
-
- Calisher CH. Medically important arboviruses of the United States and Canada. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1994;7:89–116. - "V体育平台登录" PMC - PubMed
-
- Furuta Y, Takahashi K, Fukuda Y, Kuno M, Kamiyama T, Kozaki K, Nomura N, Egawa H, Minami S, Watanabe Y, Narita H, Shiraki K. In vitro and in vivo activities of anti-influenza virus compound T-705. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:977–981. - PMC (VSports注册入口) - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports手机版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions

