The chemokine CXCL16 is highly and constitutively expressed by human bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 19415545
- PMCID: PMC2685639
- DOI: 10.1080/01902140802635517
The chemokine CXCL16 is highly and constitutively expressed by human bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
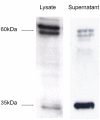
The chemokine receptor CXCR6 is highly expressed on lung-derived T cells compared to blood T cells, especially in inflammatory diseases characterised by T-cell migration to the lung. This suggests that CXCR6 is a candidate lung homing receptor. The sole ligand of CXCR6, CXCL16, has previously been shown to be expressed by alveolar macrophages. The authors hypothesized that also structural lung cells express CXCL16. CXCL16 expression was detected using real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and flow cytometry. Chemotaxis assays were used to test functionality of the secreted protein VSports手机版. Human bronchial epithelial cells secreted relatively high basal levels of CXCL16 (> 1000 pg/mL). Interferon (IFN)-gamma, but not tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha or interleukin (IL)-4, caused a modest but significant up-regulation in secretion. Airway smooth muscle and fibroblasts also expressed CXCL16, but at lower levels. Western blotting detected expression of the full-length (60-kDa) form of the chemokine in cell lysates, and the cleaved (35-kDa) form in culture supernatants. Concentrated supernatants from a bronchial epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) were chemotactic for CXCR6 expressing T cells from blood. In conclusion, these results suggest that the bronchial epithelium is an important source of constitutively expressed CXCL16, which may be involved in T-cell recruitment to the lung in health and disease. .
Figures



References (VSports注册入口)
-
- Larché M, Robinson DS, Kay A. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:450–463. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
-
- Conron M, Du Bois RM. Immunological mechanisms in sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31:543–554. - PubMed
-
- Foxman EF KE, Butcher EC. Integrating conflicting chemotactic signals: the role of memory in leukocyte navigation. J Cell Biol. 1999;147:577–587. - "V体育ios版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Rot A, von Andrian UH. Chemokines in innate and adaptive host defense: basic chemokinese grammar for immune cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:891–928. - V体育官网 - PubMed
-
- Morales J, Homey B, Vicari AP, Hudak S, Oldham E, Hedrick J, Orozco R, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, McEvoy LM, Zlotnik A. CTACK, a skin-associated chemokine that preferentially attracts skin-homing memory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:14470–14475. - PMC (V体育官网) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Grants and funding (V体育官网)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
