A gene signature-based approach identifies mTOR as a regulator of p73
- PMID: 18678646
- PMCID: PMC2547001
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00305-08
A gene signature-based approach identifies mTOR as a regulator of p73
Abstract
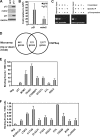
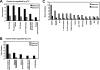
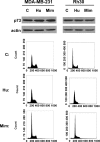
Although genomic technologies have advanced the characterization of gene regulatory networks downstream of transcription factors, the identification of pathways upstream of these transcription factors has been more challenging. In this study we present a gene signature-based approach for connecting signaling pathways to transcription factors, as exemplified by p73. We generated a p73 gene signature by integrating whole-genome chromatin immunoprecipitation and expression profiling. The p73 signature was linked to corresponding signatures produced by drug candidates, using the in silico Connectivity Map resource, to identify drugs that would induce p73 activity. Of the pharmaceutical agents identified, there was enrichment for direct or indirect inhibitors of mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. Treatment of both primary cells and cancer cell lines with rapamycin, metformin, and pyrvinium resulted in an increase in p73 levels, as did RNA interference-mediated knockdown of mTOR. Further, a subset of genes associated with insulin response or autophagy exhibited mTOR-mediated, p73-dependent expression. Thus, downstream gene signatures can be used to identify upstream regulators of transcription factor activity, and in doing so, we identified a new link between mTOR, p73, and p73-regulated genes associated with autophagy and metabolic pathways VSports手机版. .
Figures

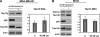


"VSports最新版本" References
-
- Akerblad, P., R. Mansson, A. Lagergren, S. Westerlund, B. Basta, U. Lind, A. Thelin, R. Gisler, D. Liberg, S. Nelander, K. Bamberg, and M. Sigvardsson. 2005. Gene expression analysis suggests that EBF-1 and PPARgamma2 induce adipogenesis of NIH-3T3 cells with similar efficiency and kinetics. Physiol. Genomics 23206-216. - PubMed
-
- Amin, A. R., R. K. Paul, V. S. Thakur, and M. L. Agarwal. 2007. A novel role for p73 in the regulation of Akt-Foxo1a-Bim signaling and apoptosis induced by the plant lectin, concanavalin A. Cancer Res. 675617-5621. - PubMed
-
- Apweiler, R., T. K. Attwood, A. Bairoch, A. Bateman, E. Birney, M. Biswas, P. Bucher, L. Cerutti, F. Corpet, M. D. Croning, R. Durbin, L. Falquet, W. Fleischmann, J. Gouzy, H. Hermjakob, N. Hulo, I. Jonassen, D. Kahn, A. Kanapin, Y. Karavidopoulou, R. Lopez, B. Marx, N. J. Mulder, T. M. Oinn, M. Pagni, F. Servant, C. J. Sigrist, and E. M. Zdobnov. 2000. InterPro—an integrated documentation resource for protein families, domains and functional sites. Bioinformatics 161145-1150. - PubMed
-
- Avruch, J., Y. Lin, X. Long, S. Murthy, and S. Ortiz-Vega. 2005. Recent advances in the regulation of the TOR pathway by insulin and nutrients. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 867-72. - PubMed
"V体育官网入口" Publication types
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
"VSports手机版" MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous (V体育官网入口)
